In the wild west of blockchain, where fortunes are made and lost in the blink of an eye, securing your smart contracts is paramount. One popular method for enhancing security is using multi-signature (multi-sig) wallets. But wielding this powerful tool improperly can be just as dangerous as leaving your digital vault unlocked. Ready to learn how to avoid the common pitfalls?
Think of the developer who loses access to their primary key, leaving a smart contract stranded with no way to make essential upgrades. Or the DAO whose funds are frozen because not enough signers are available to authorize transactions. These scenarios, while terrifying, are entirely preventable with careful planning and execution.
This blog post aims to arm you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of multi-sig wallets for contract security. We'll explore common mistakes, best practices, and actionable strategies to ensure your digital assets are safe and sound. Let's dive in and fortify your smart contract defenses!
In summary, mastering multi-sig wallets is crucial for securing smart contracts. Common pitfalls include inadequate key management, insufficient signer diversity, neglecting recovery mechanisms, and failing to properly audit implementations. By addressing these weaknesses and adopting best practices, developers can significantly enhance the resilience of their smart contracts and protect against potential exploits. Key concepts include key management, signer diversity, recovery mechanisms, audit and implementation. These aspects are critical in the effective and safe usage of multi-sig wallets within blockchain and smart contract environments.
Neglecting Key Management Best Practices
I remember once working on a project where the team decided to implement a multi-sig wallet to manage the project's treasury. We were all excited about the added security layer. However, we quickly realized that managing multiple keys across different team members presented its own set of challenges. One of the initial mistakes we made was not having a clear and documented process for key generation, storage, and rotation. We assumed everyone would handle their keys responsibly, but that wasn't necessarily the case. One team member stored their key in a plain text file on their desktop (shudder!), while another used a password manager but didn't enable two-factor authentication. This lack of standardization created vulnerabilities that could have been easily exploited.
Key management is the foundation of any secure multi-sig setup. It involves generating, storing, and using private keys responsibly. A common mistake is storing private keys on a single device or in a centralized location, defeating the purpose of a multi-sig wallet. Best practices include using hardware wallets for storing private keys, implementing strong password policies, and regularly rotating keys. Never share your private keys with anyone, and always be wary of phishing attacks. Use reputable key management solutions and consider implementing a multi-factor authentication system for accessing the wallet.
For example, imagine Alice, Bob, and Carol are the signers for a multi-sig wallet controlling a DAO's treasury. If Alice's computer is compromised, and her private key is stolen, the attacker still needs to compromise Bob and Carol to gain full control. However, if all three signers are using weak passwords or storing their keys in insecure locations, the attacker's job becomes much easier. This underscores the importance of robust key management practices for each and every signer involved.
Insufficient Signer Diversity
Insufficient signer diversity is a critical pitfall in multi-sig wallet security. It occurs when the signers of a multi-sig wallet are not sufficiently independent or diverse, creating a single point of failure or vulnerability. For instance, if all signers are members of the same team or organization, they might be susceptible to insider threats, coercion, or shared security breaches. This defeats the purpose of using a multi-sig wallet, which is intended to distribute risk and prevent unilateral control.
To avoid this, ensure that signers come from different backgrounds, have independent security practices, and are geographically dispersed. For example, a project might choose signers from the core development team, the advisory board, and a trusted community member. This diversity makes it significantly harder for an attacker to compromise enough signers to gain control of the wallet. Furthermore, consider the technical expertise of each signer. A mix of technical and non-technical signers can provide a balanced approach to security and decision-making.
Another aspect of signer diversity is the technology they use. If all signers rely on the same operating system or software, a vulnerability in that system could compromise all keys simultaneously. Encourage signers to use different operating systems, hardware wallets, and password managers to minimize this risk. By diversifying signers and their security practices, you create a more robust and resilient multi-sig wallet.
Neglecting Recovery Mechanisms
The history of cryptocurrency is littered with stories of lost keys and inaccessible wallets. While multi-sig wallets enhance security, they also introduce the risk of losing access if enough signers become unavailable. Imagine a scenario where a company's CEO, CTO, and lead developer are the signers of a multi-sig wallet. If the CEO and CTO suddenly become incapacitated, the company could be locked out of its own funds. This is where recovery mechanisms come into play.
Recovery mechanisms are pre-defined procedures for regaining access to a multi-sig wallet in emergency situations. These mechanisms typically involve appointing backup signers or implementing a time-locked recovery process. Backup signers are trusted individuals who can step in if one or more original signers become unavailable. A time-locked recovery process involves setting a delay period before a transaction can be executed, allowing the original signers to cancel the transaction if it was initiated maliciously.
Implementing a robust recovery mechanism requires careful planning and coordination. You need to identify potential scenarios that could lead to loss of access, such as death, incapacitation, or loss of keys. Then, you need to design a recovery process that is both secure and practical. This might involve consulting with legal and security experts to ensure that the recovery mechanism is legally sound and doesn't introduce new vulnerabilities. Regularly test the recovery process to ensure that it works as expected and that all signers are familiar with their roles and responsibilities.
Failing to Properly Audit Implementations
The myth that "multi-sig is automatically secure" is a dangerous one. While multi-sig wallets provide a significant security enhancement, they are only as secure as their implementation. A poorly implemented multi-sig wallet can be just as vulnerable as a single-signature wallet. This is where auditing comes in.
Auditing involves a thorough review of the multi-sig wallet's code, configuration, and operational procedures. The goal is to identify potential vulnerabilities, such as bugs in the code, misconfigured settings, or weak security practices. An audit should be performed by independent security experts who have experience with smart contract security and multi-sig wallets. The audit should cover all aspects of the multi-sig wallet, from key generation to transaction execution to recovery mechanisms.
The audit report should provide a detailed assessment of the multi-sig wallet's security posture, highlighting any vulnerabilities and recommending remediation measures. It's important to address all identified vulnerabilities promptly and thoroughly. This might involve fixing bugs in the code, updating configurations, or implementing new security practices. After implementing the remediation measures, it's a good idea to have the multi-sig wallet re-audited to ensure that the vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed. Regular audits are essential for maintaining the security of your multi-sig wallet over time.
Underestimating Gas Costs and Transaction Complexity
One hidden secret of multi-sig wallets is the increased gas costs and transaction complexity compared to single-signature wallets. Each transaction requires multiple signatures, which adds extra data to the transaction and increases the computational overhead. This can result in significantly higher gas costs, especially during periods of high network congestion. Underestimating these costs can lead to unexpected expenses and even transaction failures.
To mitigate this, it's crucial to accurately estimate the gas costs of multi-sig transactions. Use tools and techniques for gas estimation, such as profiling transactions on test networks and analyzing historical gas usage patterns. Consider optimizing the multi-sig wallet's code to reduce gas consumption. For example, you might be able to batch multiple transactions together into a single multi-sig transaction to reduce the overall gas cost.
Transaction complexity is another factor to consider. Multi-sig transactions typically involve more steps and require more coordination than single-signature transactions. This can make them more prone to errors and delays. To simplify the transaction process, use user-friendly interfaces and tools that guide signers through the necessary steps. Provide clear and concise instructions to signers, and offer support and training to help them understand the process. By carefully managing gas costs and transaction complexity, you can ensure that your multi-sig wallet is both secure and efficient.
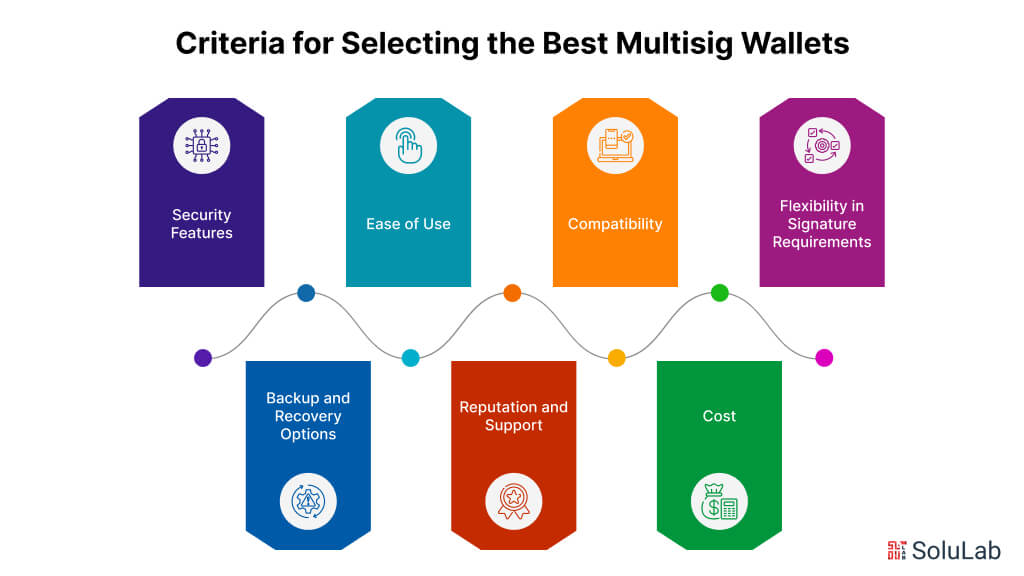
Recommendations for Choosing a Multi-Sig Wallet
Choosing the right multi-sig wallet is a critical decision that can have a significant impact on the security of your smart contracts. There are many different multi-sig wallets available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are some recommendations to help you make the right choice:
First, consider the security features of the wallet. Does it support hardware wallets for storing private keys? Does it implement multi-factor authentication? Does it have a track record of security and reliability? Second, consider the ease of use of the wallet. Is it easy to set up and configure? Is it easy for signers to use? Does it provide clear and concise instructions? Third, consider the cost of the wallet. Some multi-sig wallets are free, while others require a subscription or licensing fee. Choose a wallet that fits your budget and provides the features and support you need.
Finally, consider the reputation of the wallet's developers. Are they a reputable and trustworthy team? Do they have a history of supporting and maintaining their software? Look for wallets that are open-source and have been audited by independent security experts. By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a multi-sig wallet that provides the right balance of security, usability, and cost for your needs. Remember to thoroughly test the wallet before using it to manage real funds.
Understanding Thresholds and Quorums
Within the context of multi-sig wallets, understanding thresholds and quorums is paramount. A threshold refers to the minimum number of signatures required to execute a transaction, while a quorum is the total number of signers in the multi-sig setup. For instance, in a 3-of-5 multi-sig wallet, the quorum is 5, and the threshold is 3. This means that at least 3 out of the 5 signers must approve a transaction for it to be executed.
Choosing the right threshold and quorum is a delicate balancing act. A lower threshold makes it easier to execute transactions but also increases the risk of unauthorized access. A higher threshold makes it more difficult to execute transactions but provides greater security. The optimal threshold and quorum depend on the specific needs and risk tolerance of the organization or project using the multi-sig wallet.
For example, a DAO might choose a higher threshold to protect its treasury from malicious actors, while a development team might choose a lower threshold to facilitate faster deployments. It's important to carefully consider the trade-offs between security and usability when setting the threshold and quorum. Regularly review these settings to ensure they continue to meet your needs as your project evolves. Consider the potential consequences of losing access to keys and how the chosen threshold affects the recovery process.
Tips for Regularly Reviewing and Updating Security Protocols
Security in the blockchain space is not a "set it and forget it" kind of thing. It's a continuous process that requires regular review and updates. Multi-sig wallets are no exception. Here are some tips for regularly reviewing and updating your security protocols:
First, stay informed about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities. Subscribe to security mailing lists, follow security experts on social media, and attend security conferences. Second, regularly audit your multi-sig wallet's code, configuration, and operational procedures. Use independent security experts to perform the audits and address any identified vulnerabilities promptly. Third, regularly review and update your key management practices. Rotate your keys regularly, use strong passwords, and store your keys securely. Fourth, regularly test your recovery mechanisms. Simulate emergency scenarios and ensure that your recovery process works as expected.
Fifth, regularly review and update your signer diversity. Ensure that your signers are still independent and have strong security practices. Sixth, regularly review and update your gas cost estimations. Monitor gas prices and optimize your multi-sig wallet's code to reduce gas consumption. By following these tips, you can ensure that your multi-sig wallet remains secure and up-to-date.
Importance of Documentation and Training
Documentation and training are often overlooked but are crucial components of a successful multi-sig implementation. Clear and comprehensive documentation ensures that all signers understand their roles, responsibilities, and the procedures for using the multi-sig wallet. Training equips signers with the knowledge and skills they need to use the wallet securely and effectively.
Documentation should cover all aspects of the multi-sig wallet, from key generation to transaction execution to recovery mechanisms. It should be written in clear and concise language that is easy for all signers to understand, regardless of their technical background. Training should be hands-on and interactive, allowing signers to practice using the multi-sig wallet in a safe and controlled environment.
The training should cover topics such as key management, transaction signing, and recovery procedures. It should also emphasize the importance of security and the potential consequences of making mistakes. Regularly update the documentation and training materials to reflect any changes to the multi-sig wallet or security protocols. By providing comprehensive documentation and training, you can empower your signers to use the multi-sig wallet securely and effectively.
Fun Facts about Multi-Sig Wallets
Did you know that multi-sig wallets were initially developed as a way to improve the security of Bitcoin transactions? The idea was to require multiple signatures to authorize a transaction, making it more difficult for attackers to steal funds. The first multi-sig wallets were relatively simple, but they paved the way for the sophisticated multi-sig wallets we use today.
Another fun fact is that multi-sig wallets are not just used for securing cryptocurrencies. They are also used for managing other types of digital assets, such as domain names and intellectual property. Multi-sig wallets can even be used for governing organizations, such as DAOs, by requiring multiple members to approve decisions. The versatility of multi-sig wallets makes them a valuable tool for securing and managing digital assets in a wide range of applications.
It's also interesting to note that the concept of multi-sig security extends beyond wallets. Multi-factor authentication, a common security measure used to protect online accounts, is a form of multi-sig security. It requires multiple factors, such as a password and a security code, to verify a user's identity. This highlights the fundamental principle behind multi-sig security: distributing risk and requiring multiple approvals to prevent unauthorized access.
How to Implement Regular Security Audits
Implementing regular security audits is a proactive approach to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities in multi-sig wallet implementations. The first step is to establish a clear audit schedule. Depending on the complexity and criticality of your smart contracts, audits should be conducted at least annually, or more frequently if significant changes are made to the code.
Next, engage with reputable security firms or independent auditors who specialize in smart contract security. Provide them with comprehensive access to your code, documentation, and deployment environment. Ensure that the audit covers all aspects of the multi-sig wallet, including key management, transaction signing, and recovery mechanisms. The audit report should provide a detailed assessment of the security posture, highlighting any vulnerabilities and recommending remediation measures.
After receiving the audit report, prioritize the remediation of identified vulnerabilities. Develop a plan for addressing each vulnerability, assigning responsibilities and deadlines. Once the remediation measures have been implemented, conduct a follow-up audit to verify that the vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed. By implementing regular security audits, you can continuously improve the security of your multi-sig wallet and protect against potential exploits.
What if a Signer Loses Their Key?
The scenario of a signer losing their key is a significant concern in multi-sig wallet security. This is why having robust recovery mechanisms is essential. The first step is to have a well-defined recovery process in place that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a key loss.
The recovery process typically involves appointing backup signers or implementing a time-locked recovery process. Backup signers are trusted individuals who can step in if one or more original signers become unavailable. A time-locked recovery process involves setting a delay period before a transaction can be executed, allowing the original signers to cancel the transaction if it was initiated maliciously. The specific recovery process will depend on the configuration of your multi-sig wallet and the needs of your organization.
In the event of a key loss, the first step is to verify the identity of the signer and confirm that they have indeed lost their key. Once the key loss has been verified, the recovery process can be initiated. This might involve contacting the backup signers and requesting their signatures to authorize a transaction to move the funds to a new multi-sig wallet with new signers. The key is to have a plan in place before a key loss occurs, so that you can respond quickly and effectively.
Top 5 Mistakes to Avoid with Multi-Sig Wallets
Here's a quick list of the top 5 mistakes to avoid when using multi-sig wallets for contract security:
- Neglecting Key Management: Ensure proper generation, storage, and rotation of private keys. Use hardware wallets and strong passwords.
- Insufficient Signer Diversity: Choose signers from different backgrounds and with independent security practices.
- Neglecting Recovery Mechanisms: Implement backup signers or time-locked recovery processes to regain access in emergencies.
- Failing to Properly Audit Implementations: Conduct regular security audits by independent experts to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Underestimating Gas Costs and Transaction Complexity: Accurately estimate gas costs and optimize code to reduce gas consumption. Simplify the transaction process for signers.
Avoiding these mistakes will significantly enhance the security of your multi-sig wallet and protect your smart contracts from potential exploits. Remember to prioritize security and continuously review and update your practices.
Question and Answer Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about multi-sig wallets and their security implications:
Q: What is a multi-sig wallet and how does it enhance security?
A: A multi-sig wallet requires multiple signatures to authorize a transaction, distributing risk and preventing unilateral control. This makes it significantly harder for attackers to steal funds or compromise smart contracts.
Q: How do I choose the right number of signers for my multi-sig wallet?
A: The ideal number of signers depends on the specific needs and risk tolerance of your organization. Consider the trade-offs between security and usability. A higher number of signers provides greater security but can make transactions more difficult to execute.
Q: What should I do if one of my signers loses their private key?
A: Have a well-defined recovery process in place that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a key loss. This might involve contacting backup signers or implementing a time-locked recovery process.
Q: How often should I audit my multi-sig wallet implementation?
A: Audits should be conducted at least annually, or more frequently if significant changes are made to the code. Engage with reputable security firms or independent auditors who specialize in smart contract security.
Conclusion of Top Mistakes to Avoid with Multi-Sig Wallets for Contract Security
Multi-sig wallets are a powerful tool for enhancing the security of smart contracts, but they are not a silver bullet. Avoiding common mistakes, such as neglecting key management, insufficient signer diversity, neglecting recovery mechanisms, and failing to properly audit implementations, is crucial for realizing the full potential of multi-sig security. By following the best practices outlined in this blog post, you can significantly reduce the risk of exploits and protect your digital assets. Remember that security is a continuous process, requiring regular review and updates. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay secure!