Imagine a world where contracts are unbreakable, transparent, and execute themselves automatically. No more lengthy legal battles, no more relying on trust in intermediaries. Sounds like science fiction? Think again. This isn't just a futuristic fantasy; it's the reality that's rapidly unfolding thanks to smart contracts.
For years, industries have struggled with inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and the ever-present risk of fraud. Traditional contract systems are slow, costly, and require layers of oversight. Disputes arise, trust erodes, and progress grinds to a halt. There's a yearning for a better way, a system that's inherently fair, secure, and efficient.
The revolution is happening because of how we write and compile smart contracts. These self-executing agreements, written in code and deployed on blockchain networks, are transforming everything from finance and supply chain management to healthcare and voting systems. By automating processes, ensuring transparency, and eliminating the need for intermediaries, smart contracts are creating a more trustworthy and efficient world.
This article delves into the core of this transformation, exploring how the ability to write and compile these contracts is driving innovation across diverse sectors. We'll unpack the underlying technology, examine real-world applications, and discuss the potential challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. Join us as we explore how smart contracts are reshaping the future.
The Power of Code: My First Smart Contract
I remember the first time I tried writing a smart contract. It was daunting, staring at a blank code editor, knowing that this little piece of code could potentially control real-world assets. I chose Solidity, the most popular language for Ethereum, and started with a simple "Hello, World" equivalent – a contract that could store and retrieve a single value. The process was frustrating at times. Debugging was a challenge, and understanding the nuances of gas costs and security vulnerabilities felt like climbing a steep learning curve. However, the moment I successfully deployed that contract and interacted with it on a test network, a lightbulb went off. I realized the immense potential of this technology. It wasn't just about storing data; it was about creating trustless systems that could automate complex interactions. This firsthand experience cemented my belief in the transformative power of smart contracts. The ability to define rules and execute them automatically, enforced by the blockchain, opens up a world of possibilities for streamlining processes, reducing fraud, and building more efficient and transparent systems. It is like building the first skyscraper.
What Exactly Are Smart Contracts?
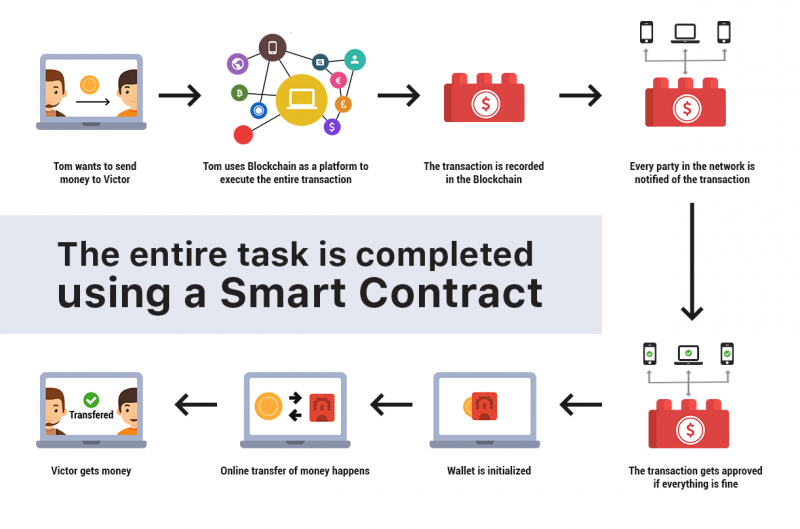
Smart contracts are essentially self-executing agreements written in code. They are deployed on a blockchain network, such as Ethereum, and automatically enforce the terms of the agreement when specific conditions are met. Think of them as digital vending machines: you put in the right amount of money (or crypto), and you get your product. There's no need for a human operator to verify the transaction or release the product. The code handles it all. The key difference is that these vending machines are decentralized and transparent. Everyone on the network can see the code of the smart contract and verify that it's working as intended. This transparency eliminates the need for trust in a central authority or intermediary. Instead, trust is built into the code itself. This is the fundamental shift that smart contracts are bringing to the world. By replacing human intermediaries with automated code, they are creating more efficient, secure, and transparent systems across various industries, from finance and supply chain to healthcare and voting.
A Brief History and the Myth of Infallibility
While the concept of smart contracts dates back to the 1990s, thanks to Nick Szabo, their real-world application only became feasible with the advent of blockchain technology. Early attempts were limited by the lack of a secure and decentralized platform to execute these contracts. Bitcoin, launched in 2009, provided a glimpse of the potential, but it was Ethereum, introduced in 2015, that truly unlocked the power of smart contracts with its Turing-complete scripting language. However, one persistent myth surrounding smart contracts is that they are infallible. This is simply not true. While the code itself may be deterministic, meaning it will always execute the same way given the same inputs, the code can still contain bugs or vulnerabilities. Several high-profile smart contract hacks, such as the DAO attack, have demonstrated the risks of poorly written or audited code. These incidents serve as a stark reminder that security is paramount and that rigorous testing and auditing are essential before deploying any smart contract to a live network. The history of smart contracts is still being written, and as the technology matures, so will the tools and techniques for ensuring their security and reliability.
The Hidden Secret: Immutability and its Implications
One of the most crucial features of smart contracts, and arguably a hidden secret behind their transformative power, is immutability. Once a smart contract is deployed to the blockchain, its code cannot be changed. This immutability is what guarantees the long-term reliability and trustworthiness of the contract. It prevents any single party from unilaterally altering the terms of the agreement or manipulating the outcome. However, this immutability also presents challenges. If a bug is discovered in a deployed contract, it cannot be directly fixed. Instead, developers must deploy a new version of the contract and migrate the data and state from the old contract to the new one. This process can be complex and costly, highlighting the importance of thorough testing and auditing before deployment. The immutability of smart contracts is a double-edged sword. It provides unparalleled security and reliability but also demands a high level of care and expertise in the development process. Understanding this hidden secret is crucial for anyone working with smart contracts to avoid costly mistakes and ensure the long-term viability of their applications. This constraint is forcing developers to up their game!
Recommendations for Embracing Smart Contracts
For those eager to dive into the world of smart contracts, here are a few recommendations to get you started. Firstly, familiarize yourself with the fundamentals of blockchain technology. Understanding how blockchains work and the principles of decentralization, consensus mechanisms, and cryptography is essential for grasping the underlying concepts of smart contracts. Next, choose a programming language to learn. Solidity is currently the most popular language for developing smart contracts on Ethereum, but other languages such as Vyper are also gaining traction. Numerous online resources, tutorials, and courses are available to help you learn Solidity. Practice is key. Start with simple smart contracts and gradually work your way up to more complex projects. Deploy your contracts to test networks to gain hands-on experience and experiment with different functionalities. Finally, stay up-to-date with the latest developments in the smart contract space. The technology is constantly evolving, so it's important to follow industry news, attend conferences, and engage with the community to stay informed and learn from others. By following these recommendations, you can equip yourself with the knowledge and skills necessary to harness the transformative power of smart contracts.
Security Considerations: Auditing and Best Practices
Security is paramount when it comes to smart contracts, given their immutable nature and the potential for significant financial consequences if vulnerabilities are exploited. Therefore, meticulous auditing and adherence to best practices are crucial throughout the development lifecycle. Smart contract audits involve a thorough review of the code by security experts to identify potential flaws, bugs, and vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. These audits typically involve both automated analysis and manual code review. Best practices for secure smart contract development include using established coding patterns, avoiding common pitfalls, and implementing robust access control mechanisms. It's also essential to keep dependencies up-to-date and to regularly monitor the contract for any suspicious activity. In addition to code audits, formal verification techniques can be used to mathematically prove the correctness and security of smart contracts. While these techniques are more complex and time-consuming, they can provide a higher level of assurance. By prioritizing security and adopting a proactive approach to auditing and best practices, developers can significantly reduce the risk of smart contract exploits and protect their users' assets.
Tips for Writing Efficient and Gas-Optimized Smart Contracts
Writing efficient and gas-optimized smart contracts is crucial for minimizing transaction costs and maximizing the scalability of decentralized applications. Gas is the unit of measurement used to calculate the amount of computational effort required to execute a smart contract on the Ethereum network. Every operation performed by a smart contract consumes gas, and users must pay for this gas in Ether (ETH). Therefore, optimizing gas consumption is essential for making smart contracts economically viable. One key tip is to minimize storage reads and writes. Storage operations are significantly more expensive than memory operations, so it's important to cache frequently accessed data in memory. Another tip is to use efficient data structures and algorithms. For example, using mappings instead of arrays can significantly reduce gas costs for certain operations. It's also important to avoid unnecessary loops and iterations. Whenever possible, try to perform operations off-chain and only write the results to the blockchain. Finally, use the latest compiler optimizations and gas analysis tools to identify potential areas for improvement. By following these tips, developers can significantly reduce the gas costs of their smart contracts and make their applications more scalable and affordable.
Testing and Debugging Strategies: Ensuring Contract Reliability
Thorough testing and debugging are essential for ensuring the reliability and correctness of smart contracts. Given the immutable nature of smart contracts, it's crucial to identify and fix any bugs or vulnerabilities before deployment. Several testing and debugging strategies can be employed to achieve this goal. Unit testing involves testing individual functions or modules of the smart contract in isolation to verify that they are working as intended. Integration testing involves testing the interactions between different parts of the contract or between the contract and other external systems. Fuzzing involves generating random inputs to the contract to uncover unexpected behavior or vulnerabilities. Debugging tools can be used to step through the execution of the contract and inspect the state of variables and memory. It's also important to test the contract on different blockchain environments, such as test networks and mainnet, to ensure that it behaves consistently across different platforms. By implementing a comprehensive testing and debugging strategy, developers can significantly increase the reliability and security of their smart contracts.
Fun Facts About Smart Contracts
Did you know that the first documented proposal for a smart contract-like system dates back to 1994, predating the creation of Bitcoin by over a decade? Nick Szabo, a computer scientist and cryptographer, coined the term "smart contracts" and envisioned them as self-executing digital contracts that could automate various business processes. Another fun fact is that the largest smart contract hack in history involved the DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) in 2016, resulting in the theft of approximately $50 million worth of Ether. This incident highlighted the importance of security audits and formal verification techniques for smart contracts. Despite these challenges, smart contracts have seen tremendous growth in recent years, with millions of contracts deployed on various blockchain platforms. They are being used for a wide range of applications, including decentralized finance (De Fi), supply chain management, healthcare, and voting systems. The future of smart contracts looks bright, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving their security, scalability, and usability. These self-executing agreements are changing the world!
How to Learn Solidity: A Step-by-Step Guide
Learning Solidity, the primary language for writing smart contracts on Ethereum, can seem daunting at first, but with a structured approach, it becomes a manageable and rewarding process. Start with the basics: Begin by understanding the fundamental concepts of programming, such as variables, data types, control flow, and functions. There are numerous online resources and tutorials available for learning these concepts. Next, familiarize yourself with the Ethereum blockchain. Understanding how Ethereum works, including concepts like gas, accounts, and transactions, is essential for writing effective smart contracts. Then, dive into Solidity syntax and semantics. Solidity is a statically typed, contract-oriented programming language, so it's important to understand its specific syntax and rules. Focus on core concepts such as contracts, functions, state variables, modifiers, and events. Practice coding smart contracts by working through tutorials and building your own simple projects. Start with basic contracts that perform simple tasks and gradually increase the complexity of your projects. Deploy your contracts to test networks, such as Ropsten or Rinkeby, to gain hands-on experience and experiment with different functionalities. Finally, stay up-to-date with the latest developments in the Solidity language. The language is constantly evolving, so it's important to follow industry news, attend conferences, and engage with the community to stay informed. Learning Solidity opens doors to a vast ecosystem of decentralized applications and opportunities to build innovative solutions on the blockchain.
What If Smart Contracts Fail? Recovery and Mitigation Strategies
Even with the best development practices, smart contracts can still fail due to unforeseen bugs, vulnerabilities, or external events. Therefore, it's crucial to have recovery and mitigation strategies in place to minimize the impact of such failures. One common strategy is to implement a "kill switch" function that allows the contract owner to temporarily disable the contract in case of an emergency. This can prevent further damage or loss of funds. Another strategy is to implement a "pause" function that allows the contract owner to temporarily pause certain functionalities of the contract, such as trading or withdrawals. This can give the contract owner time to investigate and resolve the issue without disrupting the entire system. In some cases, it may be possible to upgrade the contract to fix the bug or vulnerability. However, due to the immutability of smart contracts, upgrading a contract typically involves deploying a new version of the contract and migrating the data and state from the old contract to the new one. This process can be complex and costly, so it's important to plan for it in advance. Finally, it's essential to have a comprehensive incident response plan in place that outlines the steps to be taken in case of a smart contract failure. This plan should include clear communication channels, escalation procedures, and recovery strategies. By proactively planning for potential failures, developers can minimize the impact of smart contract failures and protect their users' assets. Planning can sometimes be hard, so a proper way to manage this is to involve external support!
Listicle: Top 5 Industries Being Transformed by Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are revolutionizing various industries by automating processes, ensuring transparency, and eliminating the need for intermediaries. Here are the top 5 industries being transformed by smart contracts: 1. Finance: Smart contracts are enabling decentralized finance (De Fi) applications, such as lending platforms, exchanges, and stablecoins, by automating financial transactions and eliminating the need for traditional financial institutions.
2. Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts are improving transparency and traceability in supply chains by tracking goods and materials from origin to consumer, reducing fraud and improving efficiency.
3. Healthcare: Smart contracts are enabling secure and transparent sharing of patient data, automating insurance claims processing, and improving the efficiency of clinical trials.
4. Real Estate: Smart contracts are streamlining real estate transactions by automating the transfer of ownership, reducing paperwork, and eliminating the need for intermediaries.
5. Voting Systems: Smart contracts are enabling secure and transparent online voting systems, reducing voter fraud and improving voter participation. The potential applications of smart contracts are vast and continue to expand as the technology matures, promising to transform even more industries in the future.
Question and Answer: Understanding Smart Contracts
Here are some common questions and answers about smart contracts:
Q: What are the benefits of using smart contracts?
A: Smart contracts offer numerous benefits, including increased transparency, improved security, reduced costs, and increased efficiency.
Q: Are smart contracts secure?
A: Smart contracts can be secure if they are properly written, audited, and tested. However, vulnerabilities can exist, so security is paramount.
Q: What programming languages are used to write smart contracts?
A: Solidity is the most popular language for Ethereum smart contracts, but other languages like Vyper are also used.
Q: Can smart contracts be updated or modified after deployment?
A: Typically, no. Once deployed, smart contracts are immutable. Updates usually require deploying a new contract and migrating data.
Conclusion of How Writing and Compiling Smart Contracts Is Changing the World
The ability to write and compile smart contracts is ushering in a new era of trust, transparency, and automation. From revolutionizing finance to streamlining supply chains, the impact of this technology is already being felt across various industries. While challenges remain, particularly around security and scalability, the potential benefits of smart contracts are undeniable. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, we can expect to see even more innovative applications emerge, further transforming the way we interact and transact in the digital world. The revolution has begun, and the future is being written, line by line, in smart contract code.