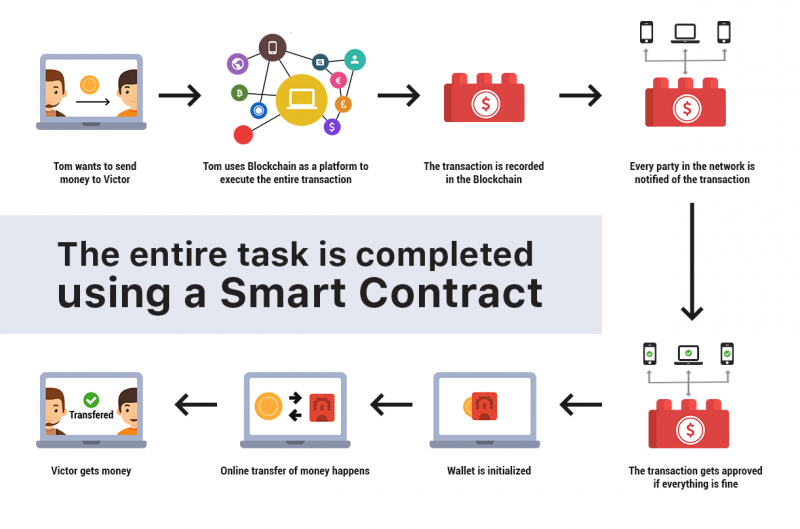
Imagine a world where agreements are automatically enforced, cutting out the middleman and ensuring transparency. Sounds like science fiction? Think again! We're diving into the world of smart contracts, a technology that's rapidly changing how we think about trust and transactions in the digital age.
Trying to wrap your head around the complexities of blockchain, coding, and legal jargon? It can feel like you're trying to decipher an ancient language. Where do you even begin, and how can you be sure you're getting accurate, up-to-date information?
This blog post is your guide to understanding what the experts are saying about getting started with smart contracts. We'll break down the key concepts, explore real-world applications, and address common misconceptions, giving you a solid foundation for navigating this exciting field.
We'll cover expert opinions on the fundamentals of smart contracts, exploring their potential, limitations, and the best ways to learn and implement them. Expect insights into the technologies they rely on, their impact across various industries, and practical advice for anyone looking to build their own decentralized applications (d Apps). Keywords include blockchain, decentralized applications, Solidity, Ethereum, security, and legal implications.
The Building Blocks: What the Experts Highlight
My first encounter with smart contracts felt a bit like stumbling upon a secret code. I remember attending a blockchain conference and being bombarded with terms like "Solidity," "gas," and EVM.It was overwhelming! But after speaking with several developers and researchers, I realized that the core concepts weren't as daunting as they initially seemed. They emphasized that understanding the underlying principles of cryptography and distributed ledgers is crucial. Smart contracts, they explained, are essentially self-executing agreements written in code and stored on a blockchain. This means they automatically enforce the terms of a contract when predetermined conditions are met. Think of it like a vending machine – you put in the correct amount of money, and you get your desired snack. No need for a human intermediary! Experts highlight that the most important aspect is the immutability and transparency they offer. Once deployed, a smart contract cannot be altered, and all transactions are publicly visible on the blockchain. This eliminates the need for trust between parties, as the contract's code serves as the ultimate arbiter. Furthermore, they stress the importance of secure coding practices, as vulnerabilities in smart contracts can lead to significant financial losses. This often involves rigorous auditing and testing before deployment. The experts’ consensus is that while the technology is still evolving, its potential to revolutionize various industries, from finance and supply chain management to healthcare and real estate, is undeniable.
What Are Smart Contracts, Really?
Experts define smart contracts as self-executing contracts written in code and stored on a blockchain. These contracts automatically enforce the terms of an agreement when specific conditions are met. Crucially, they emphasize that smart contracts aren't actually "smart" in the artificial intelligence sense. They're more like automated scripts that follow a predetermined set of rules. What makes them revolutionary is their decentralized nature and immutability. Because they reside on a blockchain, they're resistant to censorship and tampering. This fosters trust between parties who may not know each other. Experts also point out that smart contracts can automate complex processes, reduce transaction costs, and increase efficiency. For instance, in supply chain management, a smart contract could automatically release payment to a supplier once a shipment reaches its destination. In real estate, it could automate the transfer of property ownership upon completion of certain milestones. However, experts also caution against overhyping the technology. Smart contracts are only as good as the code they're based on. Bugs and vulnerabilities can lead to unintended consequences and financial losses. Therefore, they stress the importance of thorough testing and security audits. Furthermore, the legal implications of smart contracts are still being debated. Questions surrounding enforceability, liability, and regulatory compliance need to be addressed before widespread adoption can occur. Despite these challenges, experts agree that smart contracts have the potential to transform various industries and revolutionize the way we do business.
History and Myth: Tracing the Roots
The history of smart contracts is often intertwined with the early days of blockchain technology. While the term "smart contract" was coined by Nick Szabo in 1994, the concept didn't gain widespread attention until the emergence of Bitcoin and, later, Ethereum. Experts clarify that Szabo's vision was of contracts that could be embedded in hardware and software, automating the execution of agreements and reducing the need for intermediaries. However, the limitations of early blockchain platforms hindered the realization of this vision. Bitcoin, for example, offered limited scripting capabilities, making it difficult to implement complex smart contracts. It was Ethereum, launched in 2015, that truly unlocked the potential of smart contracts by introducing a more versatile scripting language called Solidity and a decentralized virtual machine capable of executing complex code. Experts often debunk the myth that smart contracts are a completely new invention. The underlying principles, such as automated execution and conditional logic, have been around for decades in various forms of computer programming. However, the combination of these principles with blockchain technology creates a unique and powerful tool for building trustless and transparent systems. They also emphasize that the history of smart contracts is still being written. New platforms, languages, and use cases are constantly emerging, pushing the boundaries of what's possible. The evolution of smart contract technology is driven by the collective efforts of developers, researchers, and entrepreneurs who are committed to building a more decentralized and efficient future.
The Hidden Secret: Security is Paramount
The "hidden secret" that experts consistently emphasize about smart contracts is the paramount importance of security. While the decentralized and immutable nature of blockchains offers inherent security advantages, smart contracts themselves are vulnerable to various attacks if not properly designed and implemented. Experts highlight that vulnerabilities in smart contract code can be exploited by malicious actors to steal funds, manipulate data, or disrupt services. Some common attack vectors include reentrancy attacks, integer overflows, and denial-of-service attacks. To mitigate these risks, experts recommend following secure coding practices, such as conducting thorough code reviews, performing rigorous testing, and using formal verification methods. They also stress the importance of auditing smart contracts by reputable security firms before deployment. Audits can identify potential vulnerabilities that might have been overlooked during the development process. Furthermore, experts advise developers to keep up-to-date with the latest security threats and best practices. The smart contract security landscape is constantly evolving, and new vulnerabilities are discovered regularly. Therefore, continuous learning and adaptation are essential for maintaining the security of smart contracts. They also point out that security is not just a technical issue but also a governance issue. Smart contract developers should consider implementing mechanisms for upgrading contracts, recovering from errors, and resolving disputes. A well-defined governance framework can help to ensure the long-term security and stability of smart contract applications.
Recommendations: Where to Start Your Journey
Experts recommend a multi-faceted approach for anyone looking to begin their journey with smart contracts. They stress the importance of building a strong foundation in blockchain technology, programming, and cryptography. Starting with blockchain fundamentals is crucial, experts say. Understanding how blockchains work, the principles of decentralization, and the different types of blockchain architectures is essential for comprehending the context in which smart contracts operate. They then recommend learning a programming language commonly used for smart contract development, such as Solidity (for Ethereum) or Vyper. Online courses, tutorials, and documentation are readily available to help aspiring developers get started. Experts also emphasize the importance of hands-on practice. Building small, simple smart contracts can help to solidify understanding and develop practical skills. They suggest experimenting with different functionalities, such as token creation, crowdfunding, and decentralized exchanges. Furthermore, experts recommend actively participating in the smart contract community. Joining online forums, attending meetups, and contributing to open-source projects can provide valuable learning opportunities and networking connections. They also advise staying up-to-date with the latest developments in the field. The smart contract landscape is constantly evolving, and new tools, techniques, and best practices are emerging regularly. Following industry news, reading research papers, and attending conferences can help to stay informed. Finally, experts caution against rushing into complex projects without proper preparation. Starting small, building a solid foundation, and gradually increasing complexity is the best approach for mastering smart contract development.
Diving Deeper: Understanding Solidity
Experts universally agree that Solidity is the go-to language for smart contract development on the Ethereum blockchain. Solidity is a high-level, contract-oriented programming language that resembles Java Script, Python, and C++. It was specifically designed for writing smart contracts that can be deployed on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Experts explain that Solidity's syntax is relatively easy to learn for programmers familiar with other object-oriented languages. However, mastering Solidity requires a deep understanding of its specific features and limitations. They highlight the importance of understanding concepts such as data types, functions, modifiers, events, and state variables. Furthermore, experts emphasize the importance of understanding how Solidity interacts with the EVM. The EVM is a decentralized virtual machine that executes smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Understanding how the EVM works is crucial for optimizing smart contract performance and avoiding common pitfalls. Experts also recommend familiarizing yourself with the different tools and frameworks available for Solidity development. These tools can help to streamline the development process, improve code quality, and enhance security. Some popular tools include Remix, Truffle, and Hardhat. They also advise developers to pay close attention to gas optimization when writing Solidity code. Gas is the unit of computation used by the EVM to execute smart contracts. Each operation in a smart contract consumes gas, and users must pay gas fees to execute their transactions. Writing efficient code that minimizes gas consumption is essential for reducing transaction costs and improving the overall user experience. They also stress the importance of writing clear and well-documented code. Smart contracts are often deployed on public blockchains, where they are visible to anyone. Therefore, it's crucial to write code that is easy to understand and maintain.
Expert Tips: Maximizing Your Learning
Experts offer a plethora of tips to help individuals maximize their learning and development in the realm of smart contracts. A common piece of advice is to embrace a "learn by doing" approach. Instead of just reading about smart contracts, actively build and deploy them. Start with simple contracts and gradually increase complexity as your understanding grows. Experts stress the importance of breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable tasks. Don't try to learn everything at once. Focus on mastering one concept at a time and gradually build your knowledge base. They also recommend setting realistic goals. Don't expect to become a smart contract expert overnight. It takes time, effort, and dedication to master this technology. They also suggest actively seeking out feedback from other developers. Share your code, ask questions, and learn from the experiences of others. Experts also highlight the importance of staying organized. Use version control systems like Git to manage your code, keep track of your progress, and collaborate with others. They also advise documenting your code thoroughly. Write comments to explain what your code does and why you made certain design decisions. This will make it easier for others (and yourself) to understand and maintain your code. Furthermore, experts recommend exploring different resources for learning about smart contracts. These resources include online courses, tutorials, documentation, and community forums. Find the resources that work best for you and use them to supplement your learning. They also emphasize the importance of persistence. Smart contract development can be challenging at times. Don't get discouraged by setbacks. Learn from your mistakes and keep moving forward.
Real-World Applications: Beyond the Hype
Experts are keen to move beyond the hype and focus on the tangible real-world applications of smart contracts. They highlight the potential of smart contracts to transform various industries, from finance and supply chain management to healthcare and real estate. In finance, experts point to the use of smart contracts for decentralized lending and borrowing platforms. These platforms allow users to borrow and lend cryptocurrency without the need for intermediaries like banks. Smart contracts can automatically match borrowers and lenders, enforce loan terms, and manage collateral. In supply chain management, experts see smart contracts as a way to improve transparency and traceability. By tracking goods and materials on a blockchain, smart contracts can provide real-time visibility into the entire supply chain. This can help to reduce fraud, improve efficiency, and ensure product quality. In healthcare, experts believe smart contracts can be used to securely store and share patient data. Patients can use smart contracts to control access to their medical records and grant permission to healthcare providers to view their data. In real estate, experts envision smart contracts automating the transfer of property ownership. Smart contracts can automatically transfer ownership upon completion of certain milestones, such as payment of the purchase price. They also emphasize that the applications of smart contracts are not limited to these industries. Smart contracts can be used in any situation where there is a need to automate agreements, reduce transaction costs, and improve trust. They also caution against overhyping the technology. Smart contracts are not a silver bullet that can solve all problems. They are just one tool in a larger toolkit. It is important to carefully consider the specific use case and determine whether smart contracts are the right solution.
Fun Facts: Did You Know?
Experts often sprinkle in fun facts to make the topic of smart contracts more engaging and accessible. Did you know that the first smart contract was created in 1994, long before the advent of blockchain technology? Nick Szabo, a computer scientist and cryptographer, coined the term "smart contract" to describe a computerized transaction protocol that executes the terms of a contract. Experts also point out that the Ethereum blockchain is not the only platform that supports smart contracts. Other platforms, such as EOS, Tezos, and Cardano, also offer smart contract functionality. Another interesting fact is that smart contracts can be used to create decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). DAOs are organizations that are governed by rules encoded in smart contracts. This allows for decentralized decision-making and transparent governance. Experts also highlight the fact that smart contracts can be used to create non-fungible tokens (NFTs). NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of items such as artwork, collectibles, and virtual real estate. Smart contracts are used to mint, transfer, and manage these NFTs. They also mention that smart contracts can be used to create prediction markets. Prediction markets allow users to bet on the outcome of future events. Smart contracts are used to manage the betting process and distribute the winnings. Furthermore, experts often note that the smart contract landscape is constantly evolving. New tools, techniques, and best practices are emerging regularly. This makes it an exciting and challenging field to be involved in.
How To: Building Your First Smart Contract
Experts emphasize that the best way to learn about smart contracts is by building one. Here's a simplified guide to creating your first smart contract using Solidity and Remix, an online IDE:
1.Set up your environment: Access Remix IDE in your web browser (remix.ethereum.org). This provides a user-friendly environment for writing, compiling, and deploying smart contracts.
2.Write your code: Create a new file in Remix and name it `Hello World.sol`. Paste the following code into the file:
```solidity
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Hello World {
string public message;
constructor(string memory initial Message) {
message = initial Message;
}
function update Message(string memory new Message) public {
message = new Message;
}
}
```
3.Compile your code: In Remix, navigate to the Solidity Compiler tab and click the "Compile Hello World.sol" button. This will translate your Solidity code into bytecode that can be executed by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
4.Deploy your contract: Navigate to the Deploy & Run Transactions tab. Choose the "Injected Provider - Meta Mask" environment if you want to deploy to a test network or the mainnet. Otherwise, use "Java Script VM (London)" for local testing.
5.Interact with your contract: Once deployed, you can interact with your contract using the functions in Remix. Enter a message in the `initial Message` field when deploying, and then use the `update Message` function to change the message.
Experts advise experimenting with different functionalities and exploring the Remix IDE to learn more about smart contract development. This simple example provides a foundation for understanding the basics of smart contract development and encourages further exploration of more complex concepts.
What If?: Exploring Potential Scenarios
Experts often explore "what if" scenarios to illustrate the potential impact and implications of smart contracts. What if all financial transactions were executed through smart contracts? Experts believe this could lead to increased transparency, reduced fraud, and lower transaction costs. What if supply chains were managed entirely by smart contracts? Experts envision a world where products can be tracked from origin to consumer, ensuring authenticity and ethical sourcing. What if voting systems were based on smart contracts? Experts suggest this could lead to more secure and transparent elections, reducing the risk of voter fraud and manipulation. What if intellectual property rights were managed by smart contracts? Experts propose a system where creators can automatically receive royalties for their work, preventing unauthorized use and distribution. What if insurance claims were processed automatically by smart contracts? Experts foresee faster and more efficient claims processing, reducing administrative overhead and improving customer satisfaction. What if healthcare records were managed by smart contracts? Experts envision patients having greater control over their medical data, granting permission to healthcare providers as needed. What if decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) became the norm? Experts propose a new form of governance where organizations are run by rules encoded in smart contracts, eliminating the need for traditional hierarchies. These "what if" scenarios highlight the transformative potential of smart contracts and encourage further exploration of their diverse applications.
Listicle: Top 5 Things to Know About Smart Contracts
Experts often distill the key takeaways about smart contracts into concise listicles:
1.Smart contracts are self-executing agreements: They automatically enforce the terms of a contract when predetermined conditions are met.
2.Smart contracts are immutable: Once deployed, a smart contract cannot be altered, ensuring transparency and trust.
3.Smart contracts are decentralized: They reside on a blockchain, making them resistant to censorship and tampering.
4.Smart contracts require secure coding practices: Vulnerabilities can lead to significant financial losses.
5.Smart contracts have diverse applications: From finance and supply chain management to healthcare and real estate.
Experts believe that these five points provide a solid foundation for understanding the core concepts of smart contracts and their potential impact on various industries. Further exploration of these concepts will lead to a deeper understanding of this transformative technology.
Question and Answer
Here are some frequently asked questions about smart contracts:
Q: Are smart contracts legally binding?
A: Experts say that the legal status of smart contracts is still evolving. While they can automate agreements, their enforceability depends on the jurisdiction and the specific terms of the contract. It's advisable to consult with legal professionals to ensure compliance with applicable laws.
Q: What are the biggest challenges facing smart contract adoption?
A: Experts identify security vulnerabilities, scalability issues, and the lack of clear regulatory frameworks as major challenges. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for widespread adoption.
Q: Do I need to be a programmer to understand smart contracts?
A: While programming skills are essential for developing smart contracts, a basic understanding of the concepts is valuable for anyone interested in blockchain technology and its applications. There are many resources available for non-programmers to learn about smart contracts.
Q: What are the alternatives to Ethereum for developing smart contracts?
A: Experts highlight other blockchain platforms such as EOS, Tezos, Cardano, and Polkadot as viable alternatives to Ethereum, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Conclusion of What Experts Say About Introduction to Smart Contracts
In conclusion, experts agree that smart contracts are a transformative technology with the potential to revolutionize various industries. While challenges remain, the benefits of increased transparency, automation, and trust make them a compelling tool for building a more decentralized and efficient future. Understanding the fundamentals, exploring real-world applications, and addressing security concerns are essential for navigating this exciting landscape.