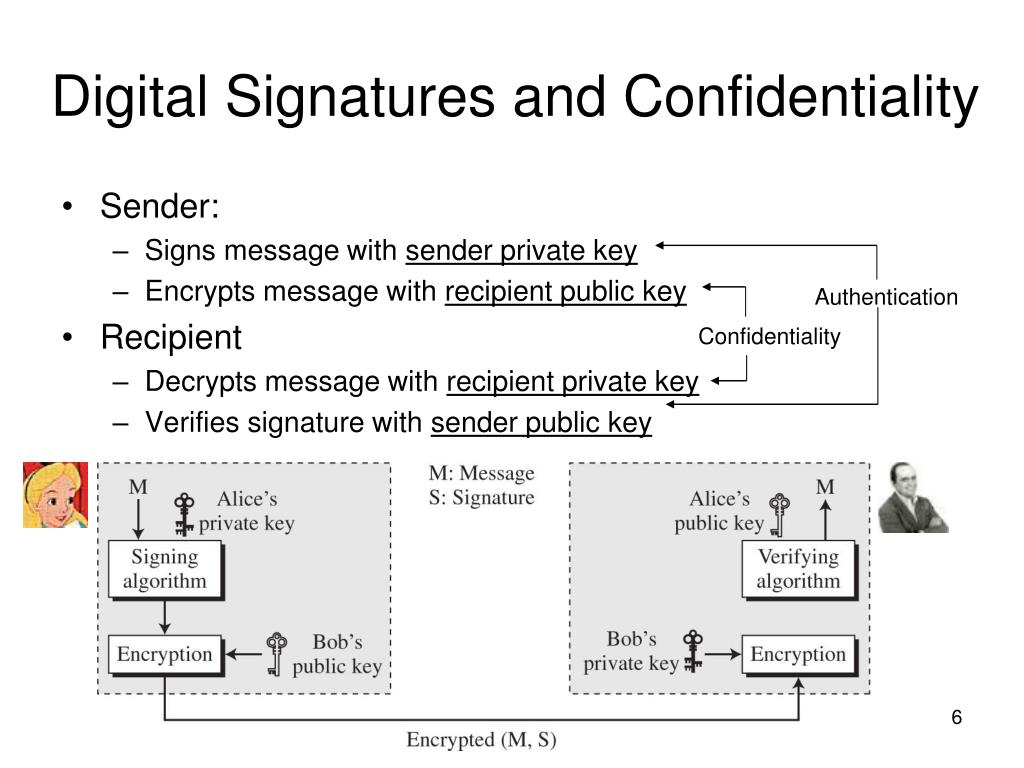
Imagine a world where contracts are signed with a click, documents are verified instantly, and your digital identity is as secure as a vault. That's the promise of digital signatures and advanced authentication. But beneath the surface of this seemingly seamless technology lies a complex web of risks and challenges that we need to navigate carefully.
Let's be honest, relying solely on usernames and passwords feels like leaving your front door unlocked. Businesses grapple with the potential for fraud, data breaches, and regulatory compliance nightmares. Individuals worry about identity theft and the misuse of their personal information. The convenience of digital transactions can quickly turn into a headache when security is compromised.
This article dives headfirst into the biggest risks and challenges surrounding digital signatures and authentication. We'll explore the vulnerabilities, the compliance hurdles, and the ever-evolving threat landscape. By understanding these challenges, we can work towards creating a more secure and trustworthy digital world.
In essence, we'll be dissecting identity theft, data breaches, regulatory compliance, key management complexities, and the ever-present threat of evolving attacks. Understanding these facets is crucial for individuals and organizations seeking to leverage digital signatures and authentication securely. This will ensure trust in digital transactions and documents. Keywords include digital signature risks, authentication challenges, data breach prevention, regulatory compliance, key management, and threat landscape.
Compliance Complexity: Navigating the Legal Maze
I remember when my company first implemented digital signatures. We were so focused on the technology that we almost completely overlooked the legal requirements. We thought, "Signatures are signatures, right?" Wrong! Each country, sometimes even each state or province, had its own specific regulations regarding the legality and enforceability of digital signatures. It was like trying to navigate a labyrinth blindfolded! We scrambled to hire a legal consultant who specialized in e-signature law. Without their guidance, we could have faced hefty fines or even had our contracts deemed invalid. That experience highlighted the critical importance of understanding the legal framework surrounding digital signatures.
Compliance is indeed a significant hurdle. Different jurisdictions have different rules about what constitutes a legally binding digital signature. This creates a challenge for multinational companies operating across borders. Standards like e IDAS in Europe aim to harmonize these regulations, but even with these efforts, complexities remain. Businesses need to ensure their digital signature solutions adhere to the specific requirements of each region they operate in, considering aspects like certificate authority recognition, signature formats, and data residency laws. Failing to do so can lead to legal challenges and invalidate digitally signed documents. Understanding these nuanced regulations is crucial for ensuring the validity and enforceability of digital agreements in a globalized world. This is why many organizations choose to implement a digital signature solution with embedded workflows and audit trails, to help demonstrate compliance.
Key Management Catastrophes: Guarding the Digital Keys
Imagine you have the most secure vault in the world, but you leave the key lying under the doormat. That's essentially what happens when key management is neglected in digital signature systems. Key management refers to the processes and technologies used to generate, store, protect, and revoke the cryptographic keys that are used to create and verify digital signatures. Weak key management practices can render even the strongest encryption algorithms useless. If private keys are compromised, attackers can forge signatures, impersonate legitimate users, and access sensitive information.
The challenge lies in striking a balance between security and usability. Keys need to be protected from unauthorized access, but they also need to be readily available to authorized users when needed. Organizations need to implement robust key management systems that include secure key storage, access controls, and procedures for key backup and recovery. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) are often used to store keys securely and perform cryptographic operations in a tamper-proof environment. Regular key rotation and revocation policies are also essential for mitigating the risk of compromised keys. Moreover, the human element cannot be ignored. Training employees on proper key handling procedures is crucial for preventing accidental or malicious key compromise. Ultimately, effective key management is the foundation of a secure digital signature system.
The History and Myth of Digital Signature Adoption
There's a common myth that digital signatures are a relatively new invention, born from the rise of the internet. In reality, the concept of using cryptography for authentication and non-repudiation dates back much further. Early forms of digital signatures were explored in the 1970s, but they weren't widely adopted until the development of public-key cryptography. The legal recognition of digital signatures was a gradual process, with various countries enacting legislation to define their legal status and enforceability.
One historical challenge was the lack of standardized protocols and interoperability. Different digital signature schemes emerged, making it difficult to verify signatures across different platforms and systems. The development of standards like PKCS (Public-Key Cryptography Standards) helped to address this issue, promoting interoperability and facilitating the adoption of digital signatures. Despite these advancements, myths and misconceptions still persist about the security and legal validity of digital signatures. Some people believe that digital signatures are easily forged or that they are not legally binding. Overcoming these misconceptions requires education and awareness-raising efforts to promote a better understanding of the underlying technology and legal framework.
Unveiling the Hidden Secrets of Authentication Protocols
Beyond the basic concept of usernames and passwords, authentication protocols have evolved significantly to address the growing threats of online fraud and identity theft. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), for instance, adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code sent to their mobile device. But even MFA is not foolproof. Attackers have developed sophisticated techniques to bypass MFA, such as SIM swapping and phishing attacks.
A hidden secret lies in the realm of adaptive authentication, which dynamically adjusts the authentication requirements based on the user's behavior, location, and device. This approach can detect suspicious activity and prompt users for additional verification when necessary. Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, offers another layer of security, but it also raises privacy concerns. The challenge is to strike a balance between security and user experience, implementing authentication protocols that are both effective and convenient. Moreover, it is critical to keep authentication protocols up to date with the latest security best practices and vulnerability patches. By understanding the hidden secrets of authentication protocols, organizations can build more robust and resilient systems.
Recommendations for Secure Digital Signatures
If you're thinking about implementing digital signatures, my biggest piece of advice is to start with a thorough risk assessment. Don't just jump into the technology without understanding the potential threats and vulnerabilities. Identify your organization's specific security needs and compliance requirements. Then, choose a digital signature solution that meets those needs and provides robust security features, such as strong encryption, secure key management, and tamper-evident audit trails.
Another crucial recommendation is to invest in employee training. Teach your employees how to use digital signatures securely and how to recognize phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics. Regularly update your security policies and procedures to reflect the latest threats and best practices. Consider using a managed security service provider to help you implement and maintain a secure digital signature infrastructure. Finally, stay informed about the latest developments in digital signature technology and regulations. The threat landscape is constantly evolving, so you need to be proactive in protecting your digital assets. By following these recommendations, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with digital signatures and reap the benefits of this powerful technology.
Choosing the Right Digital Signature Solution
Selecting the right digital signature solution is paramount. It's not just about the bells and whistles; it's about the underlying security architecture, compliance certifications, and integration capabilities. A robust solution should offer features like secure key storage, tamper-evident audit trails, and support for various digital signature standards (e.g., PAd ES, XAd ES, CAd ES). It should also be compatible with your existing IT infrastructure and business applications. Don't be afraid to ask vendors tough questions about their security practices and compliance certifications. Look for solutions that have been independently audited and certified by reputable organizations.
Consider the specific needs of your organization. Do you need to support mobile signing? Do you need to integrate with document management systems or CRM platforms? Do you need to comply with specific industry regulations, such as HIPAA or GDPR? Evaluate different solutions based on these criteria and choose the one that best fits your requirements. A well-chosen digital signature solution can streamline your workflows, improve security, and enhance your overall business efficiency. Remember to factor in long-term costs, including licensing fees, maintenance, and support. A cheap solution may seem attractive in the short term, but it could end up costing you more in the long run if it lacks essential security features or compliance certifications.
Top Tips for Strengthening Your Digital Authentication
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to strengthen your digital authentication is to enforce strong password policies. Encourage users to create complex passwords that are difficult to guess and to change their passwords regularly. Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts. Consider using a password manager to securely store and generate strong passwords. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) whenever possible. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code sent to their mobile device.
Educate your users about phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics. Teach them how to recognize suspicious emails and websites and to avoid clicking on links from untrusted sources. Regularly update your software and security patches to protect against known vulnerabilities. Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor your network for suspicious activity. Use encryption to protect sensitive data at rest and in transit. Regularly review your security logs and audit trails to identify potential security breaches. By following these tips, you can significantly strengthen your digital authentication and protect your organization from cyber threats.
The Importance of Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
In the dynamic world of cybersecurity, continuous monitoring and auditing are not just best practices; they are essential for maintaining a strong security posture. Continuous monitoring involves the ongoing collection, analysis, and reporting of security-related data. This allows you to detect and respond to threats in real-time. Auditing involves periodically reviewing your security controls and processes to ensure they are effective and compliant with relevant regulations.
By continuously monitoring your systems and networks, you can identify suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, and data exfiltration. You can then take immediate action to contain the threat and prevent further damage. Auditing your security controls and processes helps you to identify weaknesses and gaps in your security posture. You can then take corrective action to address these vulnerabilities and improve your overall security. Continuous monitoring and auditing should be an integral part of your organization's overall security strategy. They provide valuable insights into your security posture and help you to stay ahead of the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Fun Facts About Digital Signatures
Did you know that the first U.S. state to pass a law recognizing digital signatures was Utah in 1995? Or that the term "digital signature" is often used interchangeably with "electronic signature," but they are not the same thing? A digital signature is a specific type of electronic signature that uses cryptography to provide a higher level of security and assurance. The length of the cryptographic keys used in digital signatures has increased over time, reflecting the increasing computing power of attackers. Early digital signatures used 512-bit keys, while modern signatures typically use 2048-bit or 4096-bit keys.
Digital signatures are not just used for signing documents. They are also used for verifying the integrity of software updates and protecting against malware. When you download a software update from a trusted vendor, the update is typically digitally signed. This allows you to verify that the update has not been tampered with and that it comes from a legitimate source. Digital signatures are also used in blockchain technology to verify transactions and secure the distributed ledger. These fun facts illustrate the wide range of applications and the importance of digital signatures in the modern digital world.
How to Implement a Secure Digital Signature Workflow
Implementing a secure digital signature workflow requires careful planning and execution. Start by defining your organization's specific requirements and goals. What types of documents will you be signing? Who will be signing them? What compliance regulations do you need to adhere to? Once you have a clear understanding of your requirements, you can begin to design your workflow.
Choose a digital signature solution that meets your needs and integrates with your existing systems. Configure the solution to enforce your security policies and compliance requirements. Train your employees on how to use the digital signature workflow securely. Implement strong authentication measures to verify the identity of signers. Use tamper-evident audit trails to track all signing activities. Regularly review your workflow to identify potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. By following these steps, you can implement a secure digital signature workflow that streamlines your processes and protects your organization from fraud and data breaches.
What If Digital Signatures Are Compromised?
The consequences of a compromised digital signature can be severe. If a private key is compromised, attackers can forge signatures, impersonate legitimate users, and access sensitive information. This can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. In some cases, a compromised digital signature can even jeopardize national security.
If you suspect that your digital signature has been compromised, take immediate action. Revoke the compromised certificate. Notify the relevant authorities and stakeholders. Investigate the incident to determine the extent of the damage. Implement measures to prevent future compromises. Consider purchasing cyber insurance to protect against the financial losses associated with a data breach. By taking these steps, you can mitigate the damage caused by a compromised digital signature and protect your organization from further harm.
A Listicle of Digital Signature Security Best Practices
Here's a quick list of essential security best practices for digital signatures:
- Use strong encryption algorithms and key lengths.
- Implement robust key management practices.
- Enforce strong authentication measures.
- Regularly update your software and security patches.
- Train your employees on security awareness.
- Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems.
- Use tamper-evident audit trails.
- Regularly review your security policies and procedures.
- Conduct periodic security assessments.
- Stay informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
Following these best practices will significantly enhance the security of your digital signature implementation.
Question and Answer: Digital Signature Security
Q: What is the biggest threat to digital signature security?
A: The biggest threat is compromised private keys. If an attacker gains access to a private key, they can forge signatures and impersonate the legitimate owner.
Q: How can I protect my private key?
A: Store your private key securely, using a hardware security module (HSM) or a secure key management system. Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to protect your accounts. Be careful about clicking on links in emails or downloading files from untrusted sources.
Q: What is a digital certificate?
A: A digital certificate is an electronic document that verifies the identity of a signer and binds their identity to their public key. It is issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA).
Q: How can I verify the validity of a digital signature?
A: Use a digital signature validation tool or software that checks the certificate, verifies the signature, and confirms that the document has not been tampered with.
Conclusion of The Biggest Risks and Challenges in Digital Signatures and Authentication
Digital signatures and authentication technologies offer immense benefits in terms of efficiency, security, and compliance. However, it's crucial to acknowledge and address the inherent risks and challenges. From navigating the complexities of legal compliance to managing cryptographic keys securely and staying ahead of evolving threats, a proactive and comprehensive approach is essential. By prioritizing security, investing in employee training, and continuously monitoring systems, organizations can harness the power of digital signatures and authentication while mitigating potential risks and building trust in the digital realm.