Imagine a world where agreements are automatically enforced, intermediaries are eliminated, and trust is built into every transaction. Sounds like science fiction? It's not. It's the reality being shaped by the key features of smart contracts.
For too long, we've relied on cumbersome legal systems, expensive escrow services, and the inherent risks of trusting third parties to uphold their end of a bargain. Disputes arise, costs escalate, and the whole process can be fraught with uncertainty and delays. This impacts everything from simple online sales to complex international trade deals, leaving individuals and businesses vulnerable and inefficient.
Smart contracts, powered by blockchain technology, are revolutionizing the way we conduct transactions and interact with each other. Their key features – automation, transparency, security, and immutability – are fundamentally changing industries and empowering individuals in ways previously unimaginable. From streamlining supply chains to creating decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), smart contracts are paving the way for a more efficient, transparent, and trustworthy future.
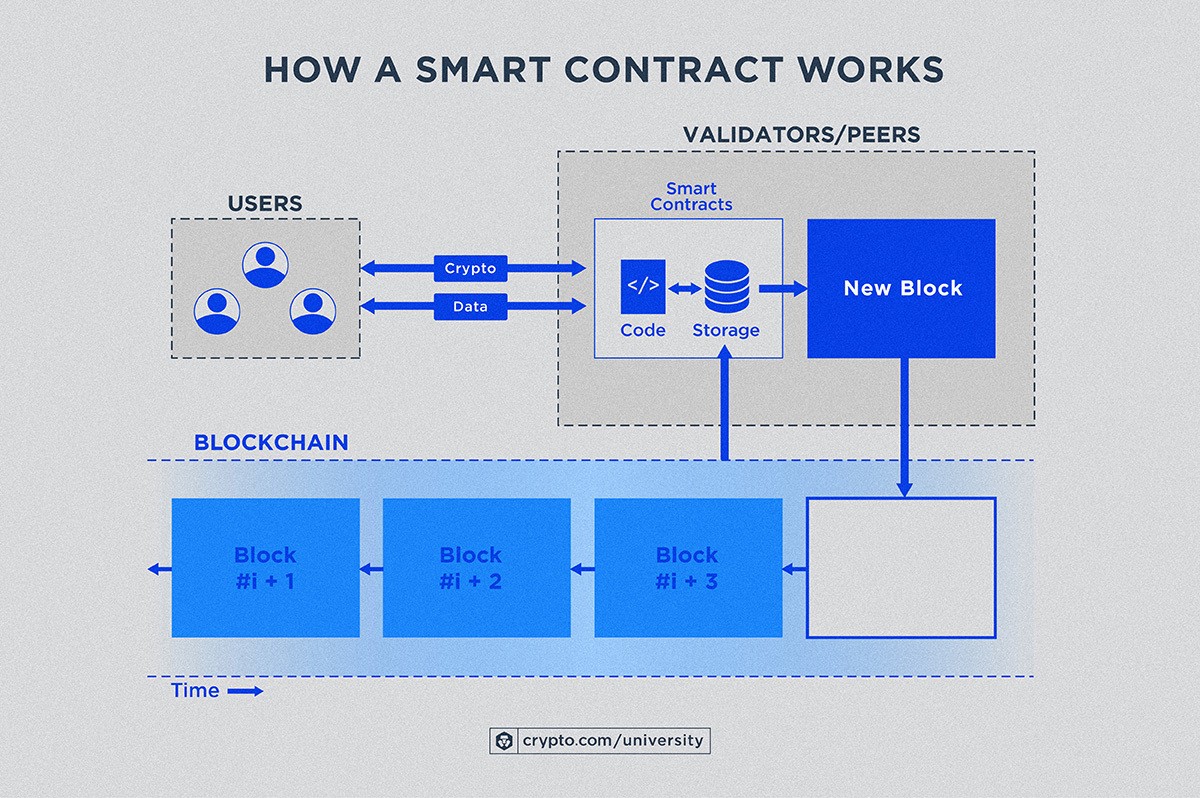
In essence, smart contracts are self-executing agreements written in code, stored on a blockchain, and automatically enforced when predetermined conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces the risk of fraud, and increases efficiency. Automation, transparency, and immutability are the cornerstones of this technological revolution, promising to reshape our world in profound ways, affecting everything from finance and supply chain management to healthcare and governance.
Automation: The Unstoppable Force
I remember the first time I truly understood the power of automation in smart contracts. I was helping a friend navigate a complex real estate transaction, watching them jump through hoops with paperwork, appraisals, and endless phone calls with lawyers and banks. The sheer inefficiency of it all was astounding. It struck me then – this entire process could be streamlined, automated, and made infinitely more secure with smart contracts. Imagine a smart contract that automatically transfers ownership and funds upon verification of a property appraisal and fulfillment of all legal requirements. No more waiting, no more intermediaries taking their cut, just a seamless, automated transaction. This is the promise of automation in smart contracts.
Beyond real estate, consider supply chain management. A smart contract can automatically trigger payments to suppliers upon delivery and verification of goods, eliminating delays and disputes. In decentralized finance (De Fi), lending and borrowing protocols are entirely automated through smart contracts, offering faster, more transparent, and more accessible financial services. Automation is not just about efficiency; it's about empowering individuals and businesses by removing barriers and creating a more level playing field.
Transparency: Shedding Light on Every Transaction
Transparency, in the context of smart contracts, refers to the ability for anyone with access to the blockchain to view the code and transaction history of a smart contract. This radical level of transparency is a game-changer. Unlike traditional contracts, which are often private and subject to interpretation, smart contracts operate in the open. All parties involved can see the terms of the agreement and the execution of those terms in real-time.
This transparency fosters trust and accountability. It reduces the potential for fraud and manipulation, as any deviations from the agreed-upon code are immediately visible. Imagine a charitable organization using a smart contract to track donations. Donors can see exactly where their money is going and how it is being used, increasing confidence and encouraging further support. In voting systems, smart contracts can ensure that every vote is recorded and counted accurately, eliminating the possibility of voter fraud. The open and transparent nature of smart contracts is essential for building trust in a decentralized world.
Immutability: A Record Etched in Stone
The history and myth around immutability are deeply intertwined with the very nature of blockchain technology. The concept of a record that cannot be altered or deleted after its creation has been a long-sought-after ideal. Think of the ancient libraries of Alexandria, whose knowledge was tragically lost to fire and destruction. The dream was always to create a system of records that would endure, uncorrupted, through time.
Blockchain and smart contracts, in a sense, realize this dream. Once a smart contract is deployed on a blockchain, its code cannot be changed. Any attempts to modify it would require creating a new contract, leaving the original intact and auditable. This immutability creates a level of trust and security that is unparalleled in traditional systems. It ensures that the rules of the agreement are fixed and cannot be manipulated by any single party. Imagine a land registry system built on a blockchain with immutable smart contracts. Land ownership records would be permanent, secure, and resistant to fraud and corruption. This is the power of immutability: to create a lasting record of truth.
Security: Fort Knox for Agreements
The hidden secret of smart contract security lies in the combination of cryptographic principles, distributed consensus mechanisms, and rigorous auditing practices. While the immutability of smart contracts offers a baseline level of security, it also means that any vulnerabilities in the code are permanent and exploitable. Therefore, writing secure smart contracts is paramount.
The process involves meticulous planning, thorough testing, and constant vigilance. Developers must be aware of common attack vectors, such as reentrancy attacks, integer overflows, and denial-of-service attacks, and implement robust defenses against them. Auditing by independent security experts is crucial to identify and address potential vulnerabilities before a smart contract is deployed. Furthermore, formal verification techniques, which use mathematical proofs to verify the correctness of smart contract code, are gaining traction as a means of ensuring a higher level of security. The security of smart contracts is not just a technical challenge; it's a collaborative effort that requires the expertise of developers, auditors, and security researchers working together to build a more secure and trustworthy future.
Use Cases: Transforming Industries
I'd recommend looking into several key use cases to understand how smart contracts are changing the world. Start with decentralized finance (De Fi), where smart contracts power lending and borrowing platforms, decentralized exchanges, and stablecoins. These applications offer greater accessibility, transparency, and efficiency compared to traditional financial systems.
Next, explore supply chain management. Smart contracts can track goods from origin to consumer, ensuring transparency, reducing fraud, and streamlining logistics. Imagine tracking a shipment of coffee beans from a farm in Colombia to a coffee shop in New York, with every step of the journey recorded on a blockchain and verified by smart contracts. This provides consumers with unprecedented insight into the origins and quality of the products they consume. Finally, consider digital identity management. Smart contracts can enable individuals to control their own data and share it securely with trusted parties, reducing the risk of identity theft and enhancing privacy. These are just a few examples of the transformative potential of smart contracts across various industries.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) represent a radical new model for organizational governance, powered by smart contracts. Imagine an organization that operates entirely on code, with rules and decision-making processes encoded in smart contracts. Members of the DAO can propose changes, vote on proposals, and allocate resources, all through a transparent and verifiable blockchain. This eliminates the need for traditional hierarchies and centralized control, empowering members to participate directly in the governance of the organization.
DAOs are being used in a wide range of applications, from venture capital funds to social networks to software development projects. They offer a more democratic and transparent way to manage organizations, fostering greater participation and accountability. However, DAOs also face challenges, such as regulatory uncertainty, security vulnerabilities, and the potential for governance failures. Despite these challenges, DAOs represent a promising vision for the future of organizations, one where power is distributed, decisions are transparent, and members are empowered to shape their own destiny.
Navigating the Challenges: A Word of Caution
When diving into smart contracts, a crucial tip is to always prioritize security. This means choosing platforms with robust security protocols, conducting thorough audits of your smart contract code, and staying informed about potential vulnerabilities. Remember, the immutability of smart contracts means that once deployed, errors cannot be easily fixed.
Another important tip is to understand the legal and regulatory landscape. Smart contracts are still a relatively new technology, and legal frameworks are evolving rapidly. It's essential to seek legal advice to ensure that your smart contracts comply with applicable laws and regulations. Finally, be prepared for the learning curve. Smart contract development requires specialized skills and knowledge. Consider investing in training and education to equip yourself with the necessary expertise. By taking these precautions, you can mitigate risks and maximize the benefits of using smart contracts.
The Importance of Audits
The importance of audits cannot be overstated. Think of it as a health check for your smart contract. Just as you wouldn't launch a product without testing it thoroughly, you shouldn't deploy a smart contract without a professional audit. Audits involve a comprehensive review of your code by independent security experts who can identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
These vulnerabilities can range from simple coding errors to complex security flaws that could allow attackers to drain funds or manipulate the contract's behavior. Auditors use a variety of tools and techniques to analyze the code, including static analysis, dynamic analysis, and fuzzing. They also review the contract's architecture and design to identify potential weaknesses. The audit report provides detailed findings and recommendations for fixing any issues. While audits are not a guarantee of absolute security, they significantly reduce the risk of exploitation and provide peace of mind. Investing in a professional audit is a crucial step in building secure and reliable smart contracts.
Fun Facts About Smart Contracts
Here's a fun fact: the term "smart contract" was coined by Nick Szabo in 1994, long before the advent of blockchain technology. Szabo envisioned smart contracts as a way to automate and enforce agreements using digital technology. However, it wasn't until the creation of Bitcoin and, later, Ethereum, that smart contracts became a practical reality.
Another interesting fact is that the first widely known real-world application of smart contracts was the DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization), a venture capital fund that was built on the Ethereum blockchain. Unfortunately, the DAO was hacked in 2016 due to a security vulnerability in its smart contract code, resulting in the theft of millions of dollars worth of Ether. This event served as a wake-up call for the smart contract community, highlighting the importance of security audits and best practices. Despite the challenges, smart contracts continue to evolve and find new applications across various industries, demonstrating their transformative potential.
Getting Started with Smart Contracts
So, how can you get started with smart contracts? The first step is to learn the basics of blockchain technology and smart contract development. There are many online resources available, including tutorials, documentation, and online courses. Once you have a basic understanding of the concepts, you can start experimenting with different programming languages and platforms.
Solidity is the most popular language for writing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. There are also other platforms and languages available, such as Vyper and Java Script-based frameworks. Experiment with different tools and find the ones that best suit your needs. Once you're comfortable writing basic smart contracts, you can start exploring more advanced concepts, such as decentralized applications (d Apps) and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). Remember to prioritize security and follow best practices to ensure that your smart contracts are secure and reliable. The journey into the world of smart contracts can be challenging, but it's also incredibly rewarding.
What If Smart Contracts Fail?
What if a smart contract fails? This is a crucial question to consider, as the consequences can be significant. Because smart contracts are immutable, meaning they cannot be easily changed once deployed, any errors or vulnerabilities in the code are permanent and exploitable. If a smart contract fails due to a bug, a security breach, or an unforeseen event, the results can range from minor inconveniences to catastrophic financial losses.
For example, the DAO hack in 2016 resulted in the theft of millions of dollars worth of Ether. In other cases, smart contract failures have led to frozen funds, corrupted data, and disrupted operations. To mitigate the risks of smart contract failures, it's essential to prioritize security, conduct thorough audits, and implement robust testing procedures. It's also important to have a contingency plan in place in case a smart contract does fail. This may involve creating a backup contract, implementing a kill switch, or seeking legal recourse. While smart contracts offer many benefits, it's crucial to be aware of the potential risks and take steps to mitigate them.
Top 5 Key Features of Smart Contracts: A Quick List
Here's a quick listicle of the top 5 key features of smart contracts:
1.Automation: Smart contracts execute automatically when predetermined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing delays.
2.Transparency: The code and transaction history of smart contracts are publicly visible on the blockchain, fostering trust and accountability.
3.Immutability: Once deployed, smart contracts cannot be changed, ensuring that the rules of the agreement are fixed and cannot be manipulated.
4.Security: Smart contracts are secured by cryptographic principles and distributed consensus mechanisms, making them resistant to fraud and tampering.
5.Efficiency: Smart contracts streamline processes, reduce costs, and increase efficiency by automating tasks and eliminating intermediaries.
These key features are transforming industries and empowering individuals in ways previously unimaginable. From decentralized finance to supply chain management to digital identity, smart contracts are paving the way for a more efficient, transparent, and trustworthy future.
Question and Answer Section: Smart Contracts Demystified
Q: What exactly is a smart contract?
A: A smart contract is a self-executing agreement written in code and stored on a blockchain. It automatically enforces the terms of the agreement when predetermined conditions are met, without the need for intermediaries.
Q: How are smart contracts different from traditional contracts?
A: Traditional contracts are typically written in legal language and require interpretation by lawyers or judges. Smart contracts are written in code and are automatically executed by computers, eliminating the need for interpretation and reducing the risk of disputes.
Q: Are smart contracts legally binding?
A: The legal status of smart contracts is still evolving. In some jurisdictions, smart contracts are recognized as legally binding agreements, while in others, their legal status is still uncertain. It's important to seek legal advice to ensure that your smart contracts comply with applicable laws and regulations.
Q: What are the main benefits of using smart contracts?
A: The main benefits of using smart contracts include increased efficiency, reduced costs, greater transparency, and enhanced security. Smart contracts automate processes, eliminate intermediaries, reduce the risk of fraud, and foster trust and accountability.
Conclusion of How Key Features of Smart Contracts Is Changing the World
The key features of smart contracts – automation, transparency, immutability, and security – are revolutionizing the way we conduct transactions and interact with each other. They are empowering individuals, transforming industries, and paving the way for a more efficient, transparent, and trustworthy future. While challenges remain, such as security vulnerabilities and regulatory uncertainty, the potential of smart contracts is undeniable. As the technology continues to evolve and mature, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of smart contracts across various sectors, shaping a world where trust is built into every transaction.