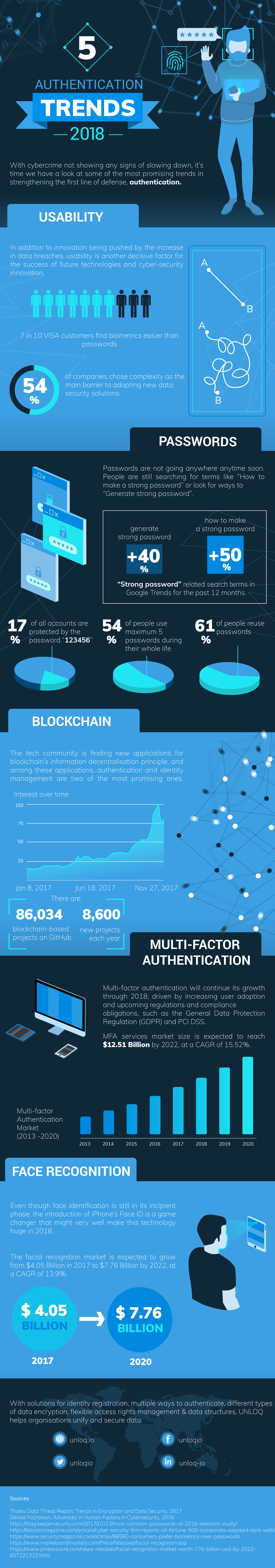
Imagine a world where verifying your identity online is as seamless and secure as showing your driver's license. The future of digital signatures and authentication is rapidly evolving, promising a more trustworthy and efficient digital landscape. But what exactly does that future hold? Experts are weighing in, and the predictions are fascinating.
The current landscape of digital security can feel like navigating a minefield. We’re constantly juggling multiple passwords, dealing with clunky two-factor authentication methods, and worrying about phishing scams. Businesses, too, face challenges – ensuring compliance, managing risk, and providing a smooth user experience all while protecting sensitive data. It’s a complex balancing act, and the stakes are high.
This blog post delves into the key trends shaping the future of digital signatures and authentication, according to industry experts. We'll explore the innovations that will enhance security, streamline processes, and ultimately, make our digital lives easier and safer. From blockchain's role to the rise of biometric authentication, prepare to discover the future of digital trust.
This article highlights the crucial shifts happening in digital signature and authentication technology. Expect to see increased adoption of blockchain for enhanced security and transparency, the growing prevalence of biometric authentication methods like facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, and the rise of passwordless authentication solutions. We’ll also touch on the importance of standardization and interoperability, as well as the increasing focus on user experience and mobile-first authentication. Keywords include: digital signatures, authentication, blockchain, biometrics, passwordless authentication, digital security, cybersecurity, digital identity, trust services.
The Rise of Biometric Authentication
The target of biometric authentication is to replace traditional methods like passwords with unique biological traits for enhanced security and user convenience. It aims to provide a frictionless and highly secure authentication experience, reducing reliance on easily compromised passwords. I remember the first time I used fingerprint scanning on my phone – it felt like something out of a sci-fi movie! Now, it’s completely commonplace, and I find myself getting frustrated when I have to type in a password. This ease of use is a major driver behind the growing popularity of biometric authentication. The technology has become more sophisticated, with advancements in facial recognition, voice recognition, and even behavioral biometrics, which analyze how you interact with your devices. Think about how your bank might recognize you not just by your face, but by the way you type or how you hold your phone. This provides an extra layer of security, making it much harder for fraudsters to impersonate you. The adoption of biometrics is also being fueled by regulatory requirements and the need for stronger authentication in various industries, including finance, healthcare, and government. Experts predict that biometric authentication will become the dominant form of authentication in the coming years, providing a more secure and user-friendly experience for everyone.
Blockchain and Digital Identity
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and immutable ledger, making it an ideal solution for managing digital identities securely and transparently. By leveraging blockchain, individuals can have greater control over their personal data, and organizations can verify identities with increased confidence. The concept of self-sovereign identity (SSI) is gaining traction, where individuals own and control their own digital identities, stored on a blockchain. This empowers individuals to selectively share their information with different entities, reducing the risk of data breaches and identity theft. Furthermore, blockchain can be used to create tamper-proof digital signatures, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of documents and transactions. This is particularly valuable in industries such as supply chain management, healthcare, and legal services, where trust and traceability are paramount. The combination of blockchain and digital identity has the potential to revolutionize how we interact online, creating a more secure, transparent, and user-centric digital ecosystem. The challenge lies in achieving interoperability between different blockchain networks and ensuring regulatory compliance. However, the benefits of this technology are undeniable, and we can expect to see widespread adoption in the years to come.
The History and Myths of Digital Signatures
The concept of digital signatures can be traced back to the early days of cryptography, with roots in the mathematical principles developed in the 1970s. However, it wasn't until the advent of public key cryptography and the development of the first digital signature algorithms that the technology truly began to take shape. One common myth is that a digital signature is simply a scanned image of a handwritten signature. In reality, a digital signature is a complex cryptographic mechanism that uses a private key to encrypt a document's hash value, creating a unique digital fingerprint. This fingerprint is then verified using the corresponding public key, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of the document. Another myth is that digital signatures are only used for high-value transactions. While they are certainly important in financial and legal contexts, digital signatures can also be used for a wide range of applications, such as signing emails, software code, and other digital documents. Understanding the history and debunking the myths surrounding digital signatures is crucial for fostering trust and adoption of this important technology. As digital signatures become more prevalent in our daily lives, it's essential to educate users about their benefits and how they work. This will help to dispel any misconceptions and ensure that digital signatures are used effectively and securely.
Hidden Secrets of Passwordless Authentication
The promise of passwordless authentication is to eliminate the reliance on traditional passwords, which are often weak, easily forgotten, and vulnerable to phishing attacks. However, the true secret of passwordless authentication lies in the diverse range of technologies that can be used to achieve this goal. From biometric authentication to security keys to one-time passcodes (OTP) sent via SMS or email, there are many ways to authenticate users without requiring them to remember a complex password. One hidden advantage of passwordless authentication is that it can significantly improve the user experience. By eliminating the need to type in a password, users can log in to their accounts more quickly and easily. This can lead to increased user satisfaction and engagement. Another secret is that passwordless authentication can actually be more secure than traditional passwords. By relying on factors such as biometrics or physical security keys, passwordless methods are less susceptible to phishing attacks and brute-force attacks. However, it's important to note that passwordless authentication is not a silver bullet. It's crucial to choose the right method for your specific needs and to implement it properly. Furthermore, it's important to have a backup plan in case the primary authentication method fails. Despite these challenges, the benefits of passwordless authentication are clear, and we can expect to see widespread adoption in the coming years.
Recommendations for Implementing Digital Signatures
When implementing digital signatures, it's crucial to start by clearly defining your goals and requirements. What types of documents do you need to sign? What level of security is required? What regulatory requirements must you comply with? Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, you can begin to evaluate different digital signature solutions. Look for solutions that are easy to use, secure, and compliant with relevant industry standards. It's also important to consider the cost of the solution, both in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance. Another important recommendation is to provide training to your users on how to use digital signatures effectively. This will help to ensure that they understand the importance of digital signatures and how to use them properly. It's also important to establish clear policies and procedures for the use of digital signatures. This will help to prevent misuse and ensure that digital signatures are used consistently across your organization. Finally, it's important to regularly review and update your digital signature implementation to ensure that it remains secure and compliant with evolving regulatory requirements. By following these recommendations, you can successfully implement digital signatures and reap the benefits of increased security, efficiency, and compliance.
The Role of Standardization and Interoperability
Standardization and interoperability are critical for the widespread adoption of digital signatures and authentication technologies. Without common standards, it can be difficult for different systems to communicate with each other, limiting the usefulness of digital signatures. Interoperability refers to the ability of different systems to work together seamlessly, regardless of the underlying technology. This is essential for ensuring that digital signatures can be recognized and validated across different platforms and applications. Several organizations are working to develop and promote standards for digital signatures and authentication, including the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). These standards define the technical specifications for digital signatures, as well as the protocols for exchanging digital signatures between different systems. One important standard is the Public-Key Infrastructure (PKI), which provides a framework for managing and distributing digital certificates. PKI is used to verify the identity of individuals and organizations and to ensure the authenticity and integrity of digital signatures. Another important standard is the e IDAS regulation in Europe, which establishes a legal framework for electronic identification and trust services. e IDAS aims to promote the cross-border recognition of digital signatures and authentication methods, making it easier for businesses and citizens to interact electronically across the European Union. By embracing standardization and interoperability, we can create a more seamless and trustworthy digital ecosystem, where digital signatures can be used with confidence.
Tips for Choosing the Right Authentication Method
Choosing the right authentication method is crucial for balancing security and user experience. There's no one-size-fits-all solution, as the best method depends on your specific needs and risk tolerance. Consider the sensitivity of the data being protected, the frequency of authentication, and the user's technical proficiency. For highly sensitive data, multi-factor authentication (MFA) is essential. This involves using two or more different authentication factors, such as something you know (password), something you have (security token), and something you are (biometrics). MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if one factor is compromised. For less sensitive data, a simpler authentication method, such as a password or a one-time passcode, may be sufficient. However, it's important to ensure that passwords are strong and that users are aware of the risks of phishing attacks. Biometric authentication is becoming increasingly popular due to its convenience and security. However, it's important to consider the privacy implications of collecting and storing biometric data. It's also important to choose a biometric method that is reliable and accurate. Ultimately, the best authentication method is one that balances security, usability, and cost. By carefully considering your needs and risk tolerance, you can choose an authentication method that provides the right level of protection for your data.
Mobile-First Authentication Strategies
With the increasing use of mobile devices, it's essential to adopt mobile-first authentication strategies. This means designing authentication methods that are optimized for mobile devices and that provide a seamless user experience on the go. One popular mobile authentication method is biometric authentication, such as fingerprint scanning or facial recognition. These methods are convenient and secure, and they can be easily integrated into mobile apps. Another mobile authentication method is push notifications. With push notifications, users can authenticate by simply tapping a button on their mobile device, without having to enter a password or OTP. Mobile apps can also leverage the device's built-in security features, such as the Secure Enclave on i OS devices and the Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) on Android devices. These features provide a secure environment for storing cryptographic keys and performing sensitive operations, such as digital signing. When designing mobile authentication methods, it's important to consider the limited screen size and input capabilities of mobile devices. Authentication methods should be simple, intuitive, and easy to use on a small screen. It's also important to consider the security risks associated with mobile devices, such as malware and device theft. Mobile apps should be designed to be resilient to these risks and to protect user data even if the device is compromised. By adopting mobile-first authentication strategies, you can provide a secure and seamless user experience on mobile devices, while also protecting user data from unauthorized access.
Fun Facts About Digital Signatures
Did you know that the first digital signature scheme was invented in 1976 by Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman, the same people who invented public key cryptography? It's a fun fact that highlights the close relationship between these two groundbreaking technologies. Another fun fact is that digital signatures are legally recognized in many countries around the world, and they have the same legal weight as handwritten signatures in many cases. This legal recognition has been instrumental in the widespread adoption of digital signatures in various industries. The electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN) in the United States and the e IDAS regulation in Europe are examples of laws that recognize the validity of digital signatures. Another interesting fact is that digital signatures are used to protect the integrity of software updates. When you download a software update, it is typically digitally signed by the software vendor. This ensures that the update has not been tampered with and that it comes from a trusted source. If the digital signature is invalid, the update is rejected, preventing potentially malicious software from being installed on your computer. These fun facts illustrate the importance and versatility of digital signatures in our digital world.
How to Secure Your Digital Signatures
Securing your digital signatures is crucial for maintaining trust and preventing fraud. One of the most important steps is to protect your private key. Your private key is the key that you use to create your digital signature, and it must be kept secret at all times. If your private key is compromised, someone could use it to create fraudulent digital signatures in your name. To protect your private key, you should store it in a secure location, such as a hardware security module (HSM) or a smart card. You should also use a strong password to protect your private key and avoid sharing it with anyone. Another important step is to use a trusted certificate authority (CA) to issue your digital certificate. A CA is an organization that verifies your identity and issues a digital certificate that binds your identity to your public key. When you use a digital certificate issued by a trusted CA, recipients of your digital signatures can be confident that the signature is authentic and that it comes from you. It's also important to regularly update your software and operating system. Software updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. By keeping your software up to date, you can reduce the risk of your digital signatures being compromised. Finally, it's important to be aware of phishing attacks. Phishing attacks are designed to trick you into revealing your private key or other sensitive information. Be wary of emails or websites that ask you to enter your private key or other personal information. By following these tips, you can secure your digital signatures and protect yourself from fraud.
What If Digital Signatures Didn't Exist?
Imagine a world without digital signatures. Online transactions would be far riskier, legal agreements would require physical presence and stacks of paperwork, and software security would be severely compromised. Without digital signatures, verifying the authenticity and integrity of digital documents would be nearly impossible. This would make it much easier for fraudsters to impersonate others, tamper with documents, and distribute malicious software. E-commerce would be significantly hampered, as consumers would be reluctant to make online purchases without a secure way to verify the identity of the seller. Legal processes would be much slower and more expensive, as all agreements would need to be signed physically. Software updates would be much riskier, as there would be no way to verify that the update is legitimate and has not been tampered with. The absence of digital signatures would also have a significant impact on government services. Citizens would need to physically visit government offices to access services that are now available online. This would be inconvenient and time-consuming, and it would also increase the cost of providing government services. In short, a world without digital signatures would be a much less secure and efficient place. Digital signatures are essential for building trust in the digital world and for enabling a wide range of online activities.
Listicle: 5 Key Benefits of Digital Signatures
Here's a listicle highlighting five key benefits of using digital signatures:
- Enhanced Security: Digital signatures provide a strong level of security, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of digital documents. They prevent tampering and forgery, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Increased Efficiency: Digital signatures streamline workflows by eliminating the need for physical signatures and paper-based processes. This saves time and money, and it allows organizations to operate more efficiently.
- Improved Compliance: Digital signatures help organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements. They provide a secure and auditable way to sign documents electronically, ensuring that they meet legal standards.
- Reduced Costs: Digital signatures reduce costs associated with printing, shipping, and storing paper documents. They also eliminate the need for physical archiving, saving valuable storage space.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Digital signatures provide a convenient and user-friendly way for customers to sign documents electronically. This improves the customer experience and makes it easier for them to do business with your organization.
These are just a few of the many benefits of using digital signatures. By implementing digital signatures, organizations can improve their security, efficiency, compliance, reduce costs, and enhance the customer experience.
Question and Answer Section on Digital Signatures
Here are some frequently asked questions about digital signatures:
Q: What is the difference between a digital signature and an electronic signature?
A: A digital signature is a specific type of electronic signature that uses cryptography to ensure the authenticity and integrity of a document. An electronic signature is a broader term that encompasses any electronic symbol or process that is used to sign a document electronically. While all digital signatures are electronic signatures, not all electronic signatures are digital signatures.
Q: Are digital signatures legally binding?
A: Yes, digital signatures are legally binding in many countries around the world. The legal validity of digital signatures is often governed by specific laws and regulations, such as the e IDAS regulation in Europe and the ESIGN Act in the United States.
Q: How do I get a digital certificate?
A: You can obtain a digital certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA). CAs are organizations that verify your identity and issue digital certificates that bind your identity to your public key. To get a digital certificate, you will typically need to provide proof of your identity and pay a fee.
Q: Can I use digital signatures on my mobile device?
A: Yes, many digital signature solutions are available for mobile devices. These solutions allow you to sign documents electronically using your mobile device, providing a convenient and secure way to sign documents on the go.
Conclusion of Experts Predict These Trends for Digital Signatures and Authentication
The future of digital signatures and authentication is bright. As technology advances and new security threats emerge, the need for secure and reliable authentication methods will only continue to grow. By embracing these predicted trends – the rise of biometrics, the integration of blockchain, the move towards passwordless solutions, and the importance of standardization – we can create a more trustworthy and efficient digital world for everyone.