Imagine a world where contracts are executed automatically, transparently, and without the need for intermediaries. No more lengthy legal battles or trust issues. This isn't a futuristic fantasy; it's the promise of smart contracts, and understanding how to write and compile them is becoming increasingly vital.
Many individuals and businesses are grappling with inefficiencies in traditional contract management. The reliance on centralized authorities, the potential for disputes, and the sheer time and cost involved can hinder innovation and progress. This is particularly noticeable when exploring new business models or attempting to streamline complex transactions.
Writing and compiling smart contracts matters in 2025 and beyond because they are the building blocks of a more efficient, transparent, and secure future. As blockchain technology matures and finds wider applications, the ability to create and deploy smart contracts will be a crucial skill for developers, entrepreneurs, and organizations seeking to leverage the power of decentralized systems.
This article explores the growing importance of smart contract development, covering its impact on various industries, the skills required, and the future landscape. Understanding smart contract principles, writing secure code, and mastering compilation techniques are essential for anyone looking to participate in the evolving world of decentralized applications (d Apps), decentralized finance (De Fi), and beyond. Key terms include: Smart Contracts, Blockchain, Decentralized Applications, Solidity, Compilation, Security.
The Growing Demand for Smart Contract Developers
My first encounter with smart contracts was during a small hackathon back in 2021. I was part of a team trying to build a decentralized voting system. Naively, we thought it would be a straightforward process. We quickly realized that writing secure and efficient smart contracts was far more complex than we initially anticipated. We struggled with gas optimization, preventing vulnerabilities like reentrancy attacks, and ensuring the contract behaved as intended under various scenarios. It was a humbling experience, but it sparked my fascination with the intricacies of smart contract development.
Fast forward to 2025, and the landscape has changed dramatically. The demand for skilled smart contract developers has exploded. Companies are actively seeking individuals who can not only write functional code but also understand the nuances of blockchain technology, security best practices, and the specific requirements of different industries. From finance and supply chain to healthcare and entertainment, smart contracts are being used to automate processes, reduce costs, and increase transparency. This widespread adoption has created a significant skills gap, making smart contract expertise a highly valuable asset. The surge in demand is driven by the potential of smart contracts to revolutionize traditional business models. By automating agreements and removing intermediaries, businesses can operate more efficiently and securely. This trend is only expected to accelerate in the coming years, making it crucial for developers to acquire the necessary skills to thrive in this emerging field. We're seeing a shift from simply building d Apps to integrating blockchain technology and smart contracts into existing business infrastructure, creating even more demand for developers who understand the practical applications of this technology.
What Are Smart Contracts and How Do They Work?
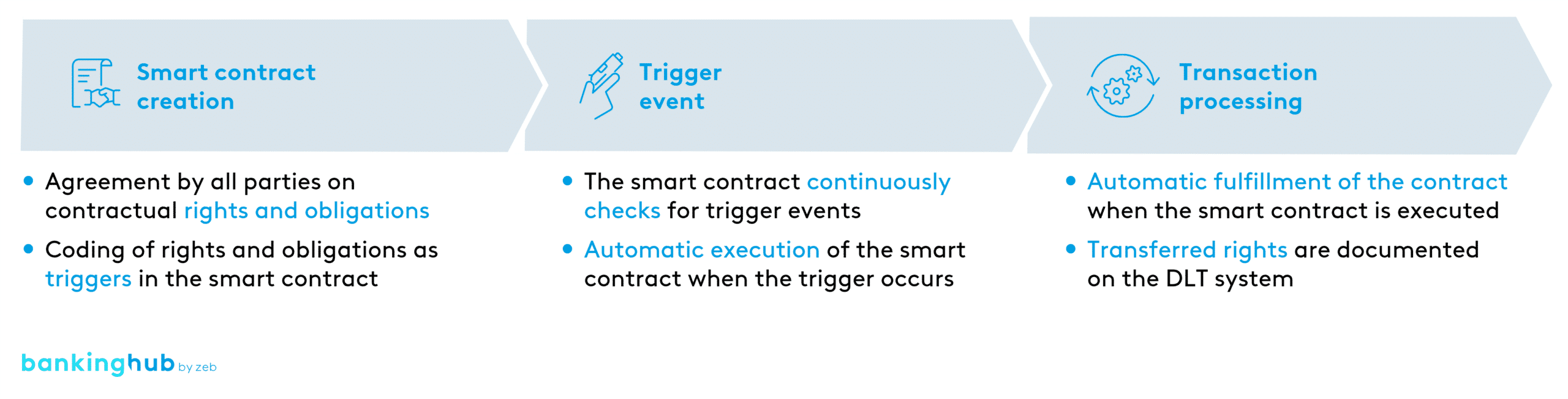
At its core, a smart contract is simply a self-executing contract written in code. It's stored on a blockchain and automatically enforces the terms of an agreement when specific conditions are met. Think of it as a digital vending machine: you put in the required input (money), and the machine dispenses the agreed-upon output (your snack) without human intervention. The beauty of smart contracts lies in their immutability and transparency. Once deployed, the code cannot be altered, and all transactions are recorded on the blockchain, making them verifiable by anyone.
This eliminates the need for trust between parties because the contract itself guarantees the outcome. Smart contracts are typically written in languages like Solidity (for Ethereum) or Rust (for Solana). These languages allow developers to define the terms of the agreement, the conditions for execution, and the actions to be taken when those conditions are met. The code is then compiled into bytecode, which is deployed to the blockchain. When a transaction triggers the contract, the bytecode is executed by the nodes on the network, ensuring that the terms are enforced. The key is that all parties agree on the contract’s code beforehand, removing ambiguity and potential for disputes. As blockchain technology evolves, we are seeing the development of more user-friendly languages and tools that make smart contract development more accessible to a wider range of developers, further driving adoption and innovation.
The History and Evolution of Smart Contracts
The concept of smart contracts predates blockchain technology. Nick Szabo, a computer scientist, first proposed the idea in 1994. He envisioned using digital contracts to automate tasks and reduce the need for intermediaries. However, it wasn't until the advent of blockchain that smart contracts became truly practical. Bitcoin, launched in 2009, laid the foundation for decentralized applications, but it was Ethereum, introduced in 2015, that truly unlocked the potential of smart contracts. Ethereum provided a platform for developers to build and deploy custom smart contracts, leading to an explosion of innovation in areas like decentralized finance (De Fi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Early smart contracts were relatively simple, focusing on basic functions like token transfers and simple escrow services. As the technology matured, developers began to explore more complex applications, such as decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, and supply chain management systems. The evolution of smart contracts has been driven by the need for greater efficiency, security, and scalability. New languages and frameworks have emerged, offering improved features and addressing the limitations of earlier platforms. The rise of layer-2 scaling solutions, such as optimistic rollups and zk-rollups, is also helping to improve the performance of smart contracts and reduce transaction fees. Looking ahead, the future of smart contracts is likely to involve greater interoperability between different blockchain networks, as well as the integration of artificial intelligence and other advanced technologies. This will enable even more complex and sophisticated applications, further transforming the way we interact with each other and the world around us.
The Hidden Secrets to Writing Secure Smart Contracts
One of the biggest challenges in smart contract development is ensuring security. Because smart contracts are immutable, vulnerabilities can be exploited by malicious actors, leading to significant financial losses. The infamous DAO hack in 2016, which resulted in the theft of millions of dollars in Ether, serves as a stark reminder of the importance of security audits and rigorous testing.
The key to writing secure smart contracts lies in understanding the common vulnerabilities and implementing best practices to prevent them. Some of the most common vulnerabilities include reentrancy attacks, integer overflows, and underflows, and denial-of-service (Do S) attacks. To mitigate these risks, developers should use secure coding practices, such as limiting external calls, using safe math libraries, and implementing access control mechanisms. Security audits by reputable firms are also essential, as they can identify potential vulnerabilities before a contract is deployed to the blockchain. Furthermore, formal verification techniques, which use mathematical proofs to verify the correctness of code, are becoming increasingly popular. Another hidden secret to smart contract security is understanding the economic incentives of attackers. By analyzing the potential attack vectors and the potential rewards for exploiting a vulnerability, developers can design contracts that are more resistant to attacks. This requires a deep understanding of game theory and mechanism design. Finally, staying up-to-date with the latest security best practices and tools is crucial, as the threat landscape is constantly evolving. The more secure and robust your contracts, the more likely they are to be trusted and adopted.
Recommendations for Aspiring Smart Contract Developers
If you're interested in becoming a smart contract developer, there are several steps you can take to get started. First, it's essential to have a solid understanding of programming fundamentals, particularly object-oriented programming. Familiarity with languages like Java Script, Python, or C++ can be helpful, as many smart contract languages share similar concepts.
Next, you'll need to learn a smart contract language like Solidity. There are many online resources available, including tutorials, documentation, and online courses. Experimenting with simple smart contracts is a great way to gain practical experience. Setting up a local development environment using tools like Truffle or Hardhat can also be beneficial, as it allows you to test and debug your code locally before deploying it to a test network. Once you have a basic understanding of Solidity, you can start exploring more advanced topics, such as gas optimization, security best practices, and design patterns. Participating in hackathons and contributing to open-source projects can also be a great way to learn from experienced developers and build your portfolio. Furthermore, networking with other developers in the blockchain community can provide valuable insights and opportunities. Attending conferences, joining online forums, and participating in local meetups can help you stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies. Finally, remember that learning to write smart contracts is an ongoing process. The field is constantly evolving, so it's important to stay curious, keep learning, and never stop experimenting. The best developers are not only technically proficient, but also creative problem-solvers who are passionate about the potential of blockchain technology.
The Importance of Gas Optimization in Smart Contracts
Gas optimization is a critical aspect of smart contract development, particularly on networks like Ethereum, where transaction fees (gas) can be significant. Gas is the unit of measure that quantifies the amount of computational effort required to execute certain operations on the Ethereum blockchain. Every transaction, including smart contract executions, requires gas, and users must pay for the gas consumed by their transactions.
The cost of gas can fluctuate depending on network congestion, making it essential to write smart contracts that are efficient and minimize gas consumption. Poorly optimized contracts can be expensive to execute, making them impractical for many applications. Gas optimization involves a variety of techniques, such as minimizing storage writes, using efficient data structures, and avoiding unnecessary loops. Developers can also use low-level operations, such as assembly code, to fine-tune their contracts for maximum efficiency. However, it's important to balance gas optimization with security considerations, as some optimization techniques can introduce vulnerabilities. Tools like Remix IDE and online gas estimators can help developers analyze the gas consumption of their contracts and identify areas for improvement. Furthermore, understanding the gas costs of different Solidity operations is crucial for writing efficient code. For example, storage writes are significantly more expensive than memory writes, so developers should strive to minimize storage interactions. The importance of gas optimization is only likely to increase as blockchain adoption grows and network congestion becomes more common. By writing gas-efficient smart contracts, developers can create applications that are more accessible and affordable for users, helping to drive the widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
Tips for Writing Readable and Maintainable Smart Contracts
While security and efficiency are crucial, writing readable and maintainable smart contracts is equally important. Code that is difficult to understand can be challenging to debug, audit, and modify, increasing the risk of errors and vulnerabilities. Writing clear and concise code is essential for collaboration and long-term maintainability.
One of the best ways to improve readability is to use meaningful variable and function names. Avoid using cryptic abbreviations or generic names that don't convey the purpose of the code. Documenting your code with comments is also crucial. Explain the purpose of each function, the expected inputs, and the possible outputs. Use comments to clarify complex logic and explain any assumptions or constraints. Following a consistent coding style can also improve readability. Use indentation, spacing, and capitalization to make the code visually appealing and easy to follow. Consider using a linter, such as Solhint, to enforce coding style guidelines and identify potential errors. Organizing your code into modular functions and classes can also improve maintainability. Avoid writing large, monolithic functions that are difficult to understand and modify. Instead, break down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable functions. Use interfaces to define the public API of your contracts and to decouple different components. Finally, consider using design patterns, such as the Factory pattern or the Proxy pattern, to improve the structure and flexibility of your code. By following these tips, you can write smart contracts that are not only secure and efficient but also easy to read, understand, and maintain, ensuring their long-term value. Clean code is always good code, especially in an environment where security and correctness are paramount.
The Role of Formal Verification in Smart Contract Security
Formal verification is a rigorous technique for proving the correctness of software, including smart contracts. It involves using mathematical models and automated tools to verify that the code meets its specifications and is free from errors and vulnerabilities. Unlike traditional testing methods, which can only uncover a limited number of potential issues, formal verification provides a comprehensive guarantee of correctness.
Formal verification techniques typically involve creating a formal specification of the smart contract's behavior, using a language like Solidity or a more specialized formal specification language. This specification describes the expected behavior of the contract under all possible conditions. The verification tool then uses mathematical reasoning to prove that the code meets the specification. If the tool finds any discrepancies, it provides a detailed explanation of the error. Formal verification can be used to detect a wide range of vulnerabilities, including reentrancy attacks, integer overflows, and logical errors. It can also be used to verify that the contract satisfies certain security properties, such as access control restrictions and data integrity constraints. While formal verification can be time-consuming and requires specialized expertise, it can provide a high level of assurance in the correctness and security of smart contracts. It is particularly useful for critical applications, such as financial instruments and identity management systems, where even a small error can have significant consequences. As blockchain technology matures, formal verification is likely to become an increasingly important tool for ensuring the reliability and security of smart contracts, especially for applications where trust is paramount.
Fun Facts About Smart Contracts
Did you know that the first smart contract was written in 1994 by Nick Szabo, long before the existence of blockchain? He called it a "self-executing contract" and envisioned it as a way to automate agreements and reduce the need for intermediaries. However, it wasn't until the advent of blockchain technology that his vision became a reality.
Another fun fact is that the term "smart contract" is somewhat of a misnomer. Smart contracts are not actually contracts in the legal sense. They are simply pieces of code that execute automatically when certain conditions are met. However, they can be used to enforce the terms of a legal agreement, making them a valuable tool for automating business processes and reducing the risk of disputes. The most expensive smart contract bug in history was the Parity Wallet hack in 2017, which resulted in the loss of over $300 million in Ether. The bug was caused by a vulnerability in the wallet's initialization code, which allowed an attacker to take ownership of the contract and drain the funds. This incident highlighted the importance of security audits and rigorous testing in smart contract development. Another interesting fact is that smart contracts can be used to create decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), which are organizations that are governed by code rather than by humans. DAOs can be used to manage everything from investment funds to social networks. The DAO concept has the potential to revolutionize the way organizations are structured and operated. However, DAOs also face significant challenges, such as governance issues and security vulnerabilities. Despite these challenges, DAOs are likely to play an increasingly important role in the future of decentralized systems. These fun facts highlight the fascinating history and potential of smart contracts, as well as the challenges and risks involved in their development.
How to Deploy a Smart Contract
Deploying a smart contract involves several steps, starting with writing and compiling the code. Once the code is compiled, it needs to be deployed to a blockchain network, such as Ethereum. This requires a blockchain client, such as Meta Mask, and some Ether to pay for the gas costs associated with the deployment.
The first step is to connect your blockchain client to the network you want to deploy to. This could be the main Ethereum network, a test network like Ropsten or Rinkeby, or a local development network like Ganache. Once you're connected, you need to transfer some Ether to your account to pay for the gas costs. The gas costs will vary depending on the complexity of the contract and the current network congestion. Next, you can use a tool like Remix IDE or Truffle to deploy the contract. These tools provide a user-friendly interface for deploying smart contracts and managing the deployment process. You'll need to specify the contract's bytecode, the gas limit, and the gas price. The gas limit is the maximum amount of gas you're willing to spend on the deployment, and the gas price is the amount of Ether you're willing to pay per unit of gas. Once you've configured the deployment settings, you can click the "deploy" button to initiate the deployment process. The blockchain client will then broadcast the deployment transaction to the network. Once the transaction is confirmed, the contract will be deployed to the blockchain, and you'll receive a transaction receipt containing the contract address. The contract address is a unique identifier that you can use to interact with the contract. Deploying a smart contract can be a complex process, but with the right tools and knowledge, it can be done relatively easily. Remember to always test your contract thoroughly before deploying it to the main network, as any bugs or vulnerabilities could have serious consequences. Also, factor in the cost of security audits to make sure that your smart contract code is safe for use.
What If Smart Contracts Fail?
The immutability of smart contracts, while a core strength, can also be a significant challenge. Once a smart contract is deployed, it cannot be altered. If a bug or vulnerability is discovered, it cannot be directly patched. This means that careful planning, rigorous testing, and security audits are essential before deploying a smart contract to the blockchain.
So, what happens if a smart contract fails? The consequences can range from minor inconveniences to significant financial losses. In some cases, the contract may simply stop functioning as intended, rendering it useless. In other cases, vulnerabilities can be exploited by malicious actors, leading to the theft of funds or the manipulation of data. The DAO hack in 2016 is a prime example of the potential consequences of smart contract failures. In that case, a vulnerability in the DAO's smart contract allowed an attacker to drain millions of dollars in Ether. While the Ethereum community eventually implemented a hard fork to restore the stolen funds, the incident served as a stark reminder of the importance of security. To mitigate the risks of smart contract failures, developers can use various techniques, such as defensive programming, formal verification, and security audits. They can also implement upgradeable contract patterns, which allow them to deploy new versions of the contract while preserving the state of the old contract. However, upgradeable contracts introduce their own complexities and risks, so they should be used with caution. In the event of a smart contract failure, it's important to have a plan in place to respond quickly and effectively. This may involve notifying users, halting the contract's execution, and deploying a fix. The best approach depends on the specific circumstances of the failure and the potential impact on users. In short, while smart contracts offer many benefits, they also come with significant risks. By taking the necessary precautions and being prepared to respond to failures, developers can minimize these risks and maximize the potential of smart contract technology.
Listicle: 5 Reasons Why You Should Learn Smart Contract Development
1.High Demand and Earning Potential: Smart contract developers are in high demand, and salaries are competitive. As the blockchain industry continues to grow, the demand for skilled developers will only increase.
2.Opportunity to Innovate: Smart contracts are a relatively new technology, and there's plenty of room for innovation. By learning smart contract development, you can be at the forefront of this exciting field and contribute to the development of new applications and business models.
3.Solve Real-World Problems: Smart contracts can be used to solve a wide range of real-world problems, from automating supply chains to creating decentralized financial systems. By learning smart contract development, you can use your skills to make a positive impact on the world.
4.Gain In-Depth Knowledge of Blockchain Technology: Smart contract development requires a deep understanding of blockchain technology. By learning to write smart contracts, you'll gain valuable insights into the inner workings of blockchain and the potential of decentralized systems.
5.Build a Strong Portfolio: Smart contract development is a practical skill that employers value. By building a portfolio of smart contract projects, you can demonstrate your skills and increase your chances of landing a job in the blockchain industry.
In conclusion, smart contract development is a valuable skill that offers many opportunities for personal and professional growth. By learning to write smart contracts, you can be at the forefront of the blockchain revolution and contribute to the development of a more decentralized and transparent future. The future is now, and smart contracts are a critical part of it.
Question and Answer about Why Writing and Compiling Smart Contracts Matters in 2025 and Beyond
Q: What are the biggest security threats to smart contracts?
A: Common security threats include reentrancy attacks, integer overflows/underflows, denial-of-service (Do S) attacks, and vulnerabilities in the logic of the contract. Rigorous testing, security audits, and formal verification can help mitigate these risks.
Q: What programming languages are commonly used for smart contract development?
A: Solidity is the most popular language for Ethereum-based smart contracts. Rust is commonly used for Solana-based contracts. Other languages like Vyper and Java Script are also used.
Q: How can I get started with smart contract development?
A: Start by learning programming fundamentals and a smart contract language like Solidity. There are many online resources available, including tutorials, documentation, and online courses. Practice writing simple smart contracts and gradually work your way up to more complex projects.
Q: What is the role of gas in smart contract execution?
A: Gas is the unit of measure that quantifies the amount of computational effort required to execute operations on the blockchain. Users must pay for the gas consumed by their transactions, so it's essential to write gas-efficient smart contracts to minimize costs.
Conclusion of Why Writing and Compiling Smart Contracts Matters in 2025 and Beyond
The ability to write and compile smart contracts is becoming increasingly critical in 2025 and beyond. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and find wider applications, smart contracts will play a central role in automating processes, reducing costs, and increasing transparency across various industries. By acquiring the necessary skills and understanding the nuances of smart contract development, you can position yourself at the forefront of this exciting field and contribute to the development of a more decentralized and secure future. Whether you're a developer, entrepreneur, or simply curious about the potential of blockchain, learning about smart contracts is an investment that will pay off in the years to come. Embrace the challenge, explore the possibilities, and become part of the smart contract revolution.