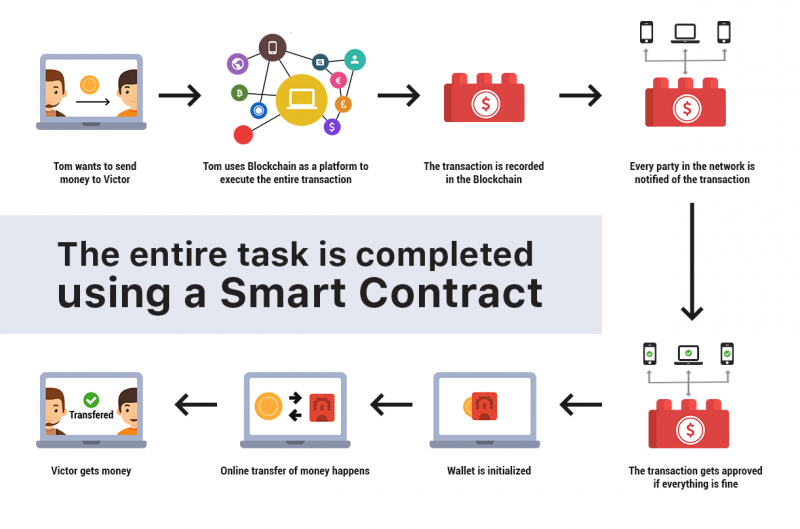
Ever wondered how those self-executing agreements everyone's talking about, smart contracts, actually make their way onto the blockchain? It's not as simple as hitting deploy.There's a whole process involved, and the experts have a lot to say about the best – and worst – ways to do it.
Let's face it, navigating the world of smart contract deployment can feel like walking through a minefield. Developers grapple with security vulnerabilities, gas optimization challenges, and the ever-present fear of deploying a flawed contract that could cost a fortune to fix (or worse, be exploited). The pressure to get it right the first time is immense, and the learning curve can be steep. Finding reliable information and best practices can also be a real struggle.
So, what do the experts say about how smart contracts are deployed? Well, the consensus is that it's a multi-stage process that demands careful planning, rigorous testing, and a deep understanding of blockchain technology. It's not just about writing code; it's about ensuring that code is secure, efficient, and behaves exactly as intended in a decentralized environment. Experts emphasize the importance of audits, formal verification, and continuous monitoring throughout the entire lifecycle of a smart contract.
In essence, successful smart contract deployment boils down to meticulous preparation, robust security measures, and ongoing vigilance. Key terms to remember are: smart contract audits, gas optimization, formal verification, deployment strategies, and security best practices. Let's dive deeper into what the experts recommend.
Understanding Smart Contract Audits
I remember the first time I heard about smart contract audits. I was at a blockchain conference, and a speaker shared a horror story about a seemingly flawless contract that got exploited, leading to a loss of millions. That's when the importance of audits truly hit home. It's not enough to just write code; you need an independent set of eyes to scrutinize it, looking for potential vulnerabilities that you might have missed.
Experts consistently advocate for comprehensive smart contract audits performed by reputable security firms. These audits involve a thorough review of the contract's code, logic, and potential attack vectors. They help identify vulnerabilities such as reentrancy attacks, integer overflows, and front-running opportunities. Think of it as a cybersecurity stress test for your smart contract. Auditors provide detailed reports with recommendations for fixing any identified issues.
The audit process typically involves static analysis (examining the code without executing it) and dynamic analysis (executing the code in a controlled environment). It's crucial to choose an auditing firm with a proven track record and expertise in the specific blockchain platform you're deploying on. While audits can be expensive, they're a necessary investment to protect against potentially catastrophic losses. After all, deploying a vulnerable smart contract is like leaving the front door of your bank vault wide open. The peace of mind that comes with a successful audit is priceless.
The Role of Gas Optimization
Gas optimization is often overlooked, but it's a critical aspect of smart contract deployment. Gas refers to the computational effort required to execute operations on the Ethereum blockchain (and similar platforms). Every transaction, including deploying and interacting with smart contracts, consumes gas. Poorly optimized code can lead to exorbitant gas fees, making your contract impractical or even unusable.
Experts emphasize the importance of writing efficient code that minimizes gas consumption. This involves techniques such as minimizing storage usage, using efficient data structures, and avoiding unnecessary loops. The Solidity compiler provides tools and optimizations that can help reduce gas costs, but developers also need to be mindful of gas considerations when designing their contracts.
Think of gas optimization as squeezing every last drop of efficiency out of your code. It's not just about saving money; it's also about improving the overall scalability and performance of the blockchain network. By reducing gas consumption, you contribute to a more efficient and sustainable ecosystem. Several tools and resources are available to help developers optimize their smart contracts for gas efficiency, including linters and gas profilers. Mastering gas optimization techniques is a crucial skill for any serious smart contract developer.
Formal Verification: A Deeper Dive
Formal verification takes smart contract security to the next level. Unlike audits, which rely on human review and testing, formal verification uses mathematical techniques to prove that a smart contract satisfies certain properties. It's like proving a theorem about your code, ensuring that it behaves as intended under all possible conditions.
Experts consider formal verification to be the gold standard for smart contract security. It can catch subtle bugs and vulnerabilities that might be missed by audits or testing. However, formal verification is also more complex and time-consuming than traditional methods. It requires specialized expertise and tools, and it's not always feasible for all types of smart contracts.
Despite the challenges, formal verification is becoming increasingly popular, especially for high-value contracts that manage significant amounts of assets. Several tools and frameworks are available to support formal verification, including model checkers and theorem provers. While it may seem daunting at first, learning the basics of formal verification can significantly enhance your understanding of smart contract security.
Deployment Strategies: Testnets and Mainnet
Choosing the right deployment strategy is crucial for a successful smart contract launch. Experts recommend deploying to testnets first before going live on the mainnet. Testnets are replicas of the mainnet that allow developers to experiment with their contracts without risking real funds. Think of it as a sandbox where you can test and debug your code in a safe environment.
There are several testnets available, such as Ropsten, Rinkeby, and Goerli. Each testnet has its own characteristics and advantages. It's important to choose a testnet that closely resembles the mainnet environment. After thoroughly testing your contract on a testnet, you can then deploy it to the mainnet, where it will interact with real users and assets.
The deployment process itself involves compiling the contract code and deploying it to the blockchain using a wallet or deployment tool. It's important to carefully review the deployment parameters, such as the gas price and gas limit, to ensure that the deployment transaction is successful. Monitoring your contract after deployment is also crucial to identify and address any issues that may arise. A well-defined deployment strategy can significantly reduce the risk of errors and ensure a smooth launch.
Security Best Practices: A Checklist
Adhering to security best practices is paramount for developing and deploying secure smart contracts. Experts recommend following a comprehensive security checklist that covers all stages of the development lifecycle. This checklist should include items such as input validation, access control, error handling, and data encryption.
Input validation is crucial to prevent malicious users from injecting harmful data into your contract. Access control mechanisms should be implemented to restrict access to sensitive functions and data. Error handling should be robust to prevent unexpected behavior and ensure that errors are handled gracefully. Data encryption can protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
In addition to these basic practices, it's also important to stay up-to-date with the latest security threats and vulnerabilities. The blockchain security landscape is constantly evolving, and new attack vectors are discovered regularly. By staying informed and following security best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of your smart contracts being compromised.
Tips for Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Smart contract development is fraught with potential pitfalls. Experts advise developers to be aware of these common mistakes and take steps to avoid them. One common pitfall is neglecting to thoroughly test the contract. Testing is crucial to identify and fix bugs before deployment.
Another common pitfall is failing to properly handle errors. Unhandled errors can lead to unexpected behavior and vulnerabilities. It's also important to avoid hardcoding sensitive data into the contract. Hardcoded data can be easily discovered and exploited.
Finally, developers should be wary of relying on external data sources without proper validation. External data can be manipulated or compromised, leading to incorrect or malicious behavior. By being aware of these common pitfalls and taking steps to avoid them, developers can significantly improve the security and reliability of their smart contracts.
The Importance of Continuous Monitoring
Even after a smart contract has been deployed, continuous monitoring is essential. Experts emphasize that monitoring is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Monitoring helps detect anomalies, security breaches, and performance issues. It's like having a security guard watching over your contract 24/7.
Monitoring tools can track key metrics such as gas consumption, transaction volume, and error rates. They can also alert you to suspicious activity, such as unusually large transactions or unexpected contract behavior. By continuously monitoring your smart contract, you can quickly identify and respond to any problems that may arise, minimizing the potential for damage.
Fun Facts About Smart Contract Deployment
Did you know that the first smart contract was proposed by Nick Szabo in 1994, long before the advent of blockchain technology? Szabo envisioned smart contracts as self-executing agreements that could automate various aspects of commerce and legal contracts. However, it wasn't until the emergence of blockchain that smart contracts became a reality.
Another fun fact is that the term "smart contract" is somewhat of a misnomer. Smart contracts are not actually contracts in the legal sense of the word. They are simply pieces of code that execute automatically when certain conditions are met. Despite the name, smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize many industries, from finance to supply chain management.
How to Secure Your Deployment Process
Securing the smart contract deployment process is just as important as securing the contract itself. Experts recommend using secure deployment tools and practices to prevent unauthorized access or modification of the contract code. This includes using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and secure communication channels.
It's also important to carefully review the deployment scripts and configurations to ensure that they are free of errors or vulnerabilities. Before deploying to the mainnet, consider using a hardware wallet to sign the deployment transaction. A hardware wallet provides an extra layer of security by storing your private keys offline. By taking these precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of your deployment process being compromised.
What If a Contract is Deployed Incorrectly?
The question on everyone's mind: What happens if a smart contract is deployed incorrectly? Experts emphasize the importance of having a contingency plan in place to deal with such situations. In some cases, it may be possible to upgrade the contract or fix the bug through a patch. However, this requires careful planning and execution to avoid introducing new vulnerabilities.
In other cases, it may be necessary to abandon the contract and deploy a new one. This can be a costly and time-consuming process, but it may be the only option if the contract is severely flawed or vulnerable. Having a clear understanding of the potential risks and having a contingency plan in place can help minimize the damage in case of an incorrect deployment.
Listicle: Top 5 Smart Contract Deployment Mistakes
1.Failing to conduct thorough audits: Audits are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities.
2.Neglecting gas optimization: High gas fees can make your contract unusable.
3.Ignoring formal verification: Formal verification can catch subtle bugs.
4.Skipping testnet deployments: Testnets allow you to experiment without risking real funds.
5.Ignoring security best practices: Security best practices are essential for preventing attacks.
Question and Answer
Q: What's the biggest mistake developers make when deploying smart contracts?
A: Experts agree that the biggest mistake is failing to conduct thorough security audits before deployment. This can lead to devastating consequences if vulnerabilities are exploited.
Q: How important is gas optimization?
A: Gas optimization is extremely important. Poorly optimized contracts can be prohibitively expensive to use, hindering adoption and functionality.
Q: Should I use formal verification?
A: Formal verification is highly recommended for critical smart contracts that manage significant assets or control important functions. While more complex, it provides a higher level of assurance.
Q: What's the best way to learn about smart contract security?
A: Start by studying common vulnerabilities and security best practices. Take online courses, read security blogs, and participate in blockchain security communities. Hands-on experience is also crucial.
Conclusion of What Experts Say About How Smart Contracts Are Deployed
In conclusion, smart contract deployment is a complex process that requires careful planning, rigorous testing, and a deep understanding of security best practices. By following the advice of experts and adhering to a comprehensive deployment strategy, developers can significantly reduce the risk of errors and vulnerabilities, paving the way for secure and reliable smart contracts that can transform industries.