Ever feel like you're missing out on the future? Like everyone else is speaking a language you haven't learned yet? That might be how you feel about smart contracts – these lines of code are quietly revolutionizing everything from finance to supply chains. But don't worry, you're not alone, and it's not as intimidating as it sounds!
Trying to wrap your head around smart contracts can feel like navigating a maze of technical jargon. Where do you even begin? Sifting through endless articles and tutorials can be overwhelming, leaving you feeling more confused than when you started. You might be asking yourself: What programming language do I need to learn? Are they even safe? And how can I use them in the real world?
This guide is designed to be your friendly starting point. We'll break down smart contracts into bite-sized pieces, explaining what they are, how they work, and how you can start exploring this exciting technology today. No prior coding experience is required – we'll focus on the fundamental concepts and point you in the right direction for further learning.
Think of this as your introductory course to the world of smart contracts. We'll explore their definition, real-world applications, the key concepts behind them, and resources to help you take your first steps. Get ready to unlock the potential of this transformative technology!
What Exactly Are Smart Contracts?
My first encounter with smart contracts was a bit like staring at a blank canvas. I understood the concept in theory – self-executing agreements written in code – but the practical applications felt distant and abstract. I remember thinking, "Okay, this is cool, but how does this actuallyhelpsomeone?"
It wasn't until I stumbled upon a project using smart contracts to automate royalty payments for musicians that things clicked. Instead of relying on complex legal agreements and intermediaries, the smart contract automatically distributed royalties to the artists based on the number of streams their songs received. This cut out middlemen, ensured transparency, and guaranteed fair compensation. This is how to get started with what are smart contracts today, right? The process is simple in essence.
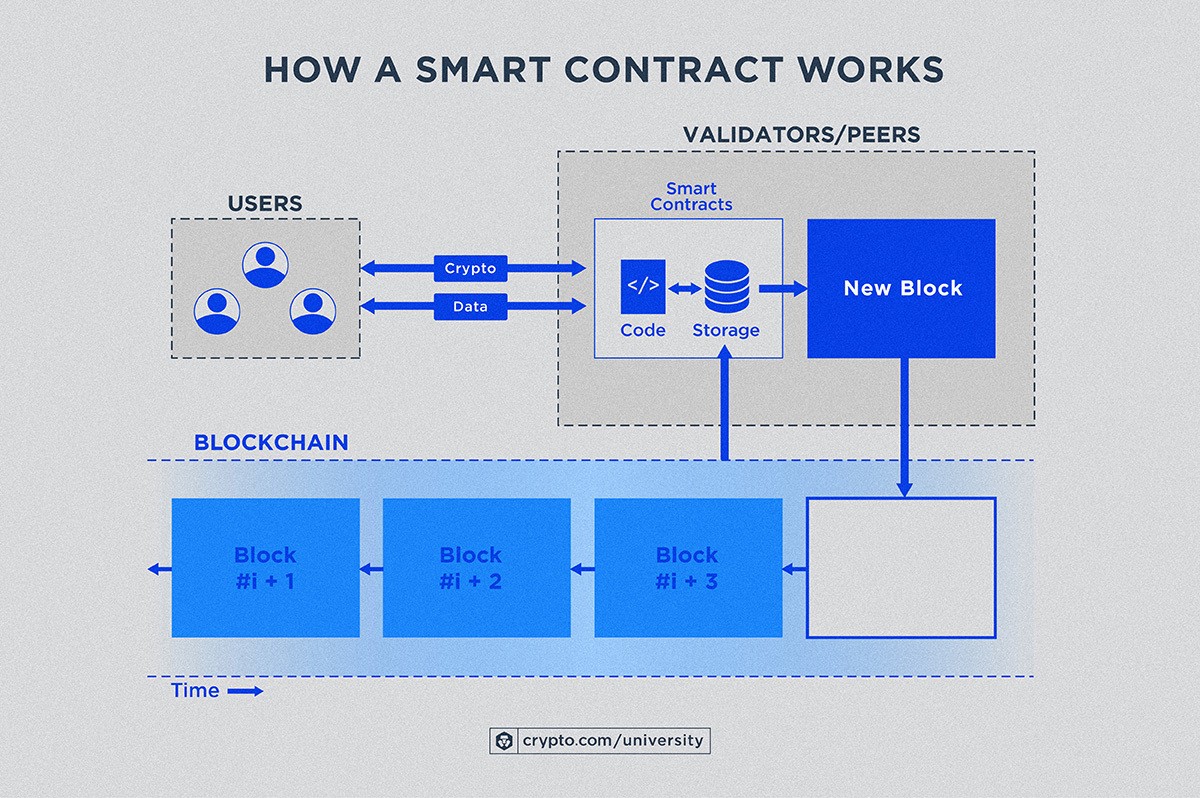
Suddenly, smart contracts weren't just abstract code; they were a powerful tool for creating fairer, more efficient systems. That experience taught me that understanding the potential of smart contracts requires seeing them in action, exploring real-world use cases, and understanding the problems they solve. Think of smart contracts as digital vending machines for services or agreements. You put in the right "payment" (data or cryptocurrency), and the contract automatically dispenses the agreed-upon outcome. This removes the need for a trusted intermediary, such as a lawyer or escrow service, making the process faster, cheaper, and more transparent. Ethereum is the most popular blockchain for deploying smart contracts, but other platforms like Cardano and Solana are also gaining traction. Ultimately, the "smart" part comes from the logic programmed into the contract. It's this logic that dictates the terms of the agreement and ensures that it is executed automatically when the conditions are met.
Why Should You Care About Smart Contracts?
How to get started with what are smart contracts today is the key question we need to answer! Smart contracts are essentially self-executing agreements written in code. They automatically enforce the terms of a contract when pre-defined conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of fraud or manipulation. Imagine a world where buying a house is as simple as transferring cryptocurrency and the ownership is automatically updated on a blockchain. Or a supply chain where every step of the process is tracked and verified by smart contracts, ensuring transparency and accountability. That's the potential of smart contracts.
At their core, smart contracts address the fundamental problems of trust and efficiency. They automate processes, reduce costs, and create more transparent systems. While still in their early stages, they are already being used in various industries, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and real estate. As the technology matures and adoption increases, smart contracts are poised to transform the way we interact and do business.
The real-world impact of smart contracts is already visible. For example, Decentralized Finance (De Fi) platforms use smart contracts to offer lending, borrowing, and trading services without the need for traditional financial institutions. Similarly, supply chain companies use smart contracts to track goods from origin to delivery, ensuring authenticity and reducing counterfeiting. So, getting started with understanding smart contracts is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for anyone who wants to stay ahead of the curve.
The History and Myths of Smart Contracts
The idea of "smart contracts" actually predates blockchain technology. Nick Szabo, a computer scientist, first proposed the concept in 1994, long before Bitcoin was even a twinkle in Satoshi Nakamoto's eye. Szabo envisioned smart contracts as a way to automate and enforce agreements electronically, reducing the need for intermediaries. He used the example of a vending machine, where the user inserts money and receives a product without needing a human attendant. This is what to get started with what are smart contracts today!
However, the technology to truly realize the potential of smart contracts didn't exist until the emergence of blockchain. Blockchain provides the secure, decentralized, and transparent platform needed to execute smart contracts in a trustworthy manner. One common myth about smart contracts is that they are completely autonomous and require no human intervention. While smart contracts do automate the execution of agreements, they still require careful design, development, and auditing by humans. Another misconception is that smart contracts are immune to bugs or vulnerabilities. Like any software code, smart contracts can contain errors that can be exploited by malicious actors. That's why thorough testing and security audits are crucial before deploying a smart contract.
Finally, some people believe that smart contracts will completely replace traditional contracts. While smart contracts offer significant advantages in certain situations, they are not a replacement for all types of agreements. Traditional contracts are often necessary for complex or nuanced situations that require human judgment and interpretation.
However, Smart contracts are revolutionizing industries by automating processes, and by being transparent by design.
The Hidden Secrets of Smart Contracts
One of the best kept secrets of smart contracts is their ability to create decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). DAOs are essentially internet-native companies or organizations that are governed by rules encoded in smart contracts. Instead of relying on a traditional hierarchical structure, DAOs allow token holders to vote on proposals and make decisions collectively. This can lead to more democratic and transparent organizations. You can use this to get started with what are smart contracts today!
Another secret is the power of composability in the smart contract ecosystem. Because smart contracts are open source and publicly auditable, they can be easily combined and integrated with each other. This allows developers to build complex applications by leveraging existing smart contracts, rather than starting from scratch. This composability fosters innovation and accelerates the development of new decentralized applications. However, the true power of smart contracts lies in their ability to create trust in a trustless environment. By encoding the rules of an agreement in code and executing it on a decentralized blockchain, smart contracts eliminate the need for trust between parties. This is particularly valuable in situations where the parties do not know each other or do not have a prior relationship. However, one thing that is not talked about is the need for gas fees. Gas fees are transaction fees paid to miners on the blockchain to execute smart contracts. These fees can fluctuate depending on network congestion and the complexity of the contract, which can be a barrier to entry for some users. Understanding gas fees and optimizing smart contracts for efficiency is crucial for minimizing costs. It's also important to keep an eye on scalability solutions like Layer 2 scaling for Ethereum, which aim to reduce gas fees and improve transaction speeds.
Recommendations for Getting Started with Smart Contracts
The best way to learn about smart contracts is to dive in and start experimenting. There are several online platforms and tools that make it easy to get started, even if you don't have any prior coding experience. Some of the most popular platforms include Remix IDE, Truffle, and Hardhat. Remix IDE is a browser-based IDE that allows you to write, compile, and deploy smart contracts directly from your web browser. It's a great option for beginners because it's easy to use and doesn't require any setup. This is how to get started with what are smart contracts today!
Truffle is a development framework that provides a suite of tools for building, testing, and deploying smart contracts. It's a more advanced option than Remix IDE, but it offers more flexibility and control. Hardhat is another popular development environment that is similar to Truffle. It's known for its speed and efficiency. In addition to these platforms, there are also many online courses and tutorials that can help you learn about smart contracts. Some popular options include Crypto Zombies, which is a free interactive course that teaches you how to build a zombie-themed game using Solidity, the most popular programming language for writing smart contracts on Ethereum. Another great resource is the Ethereum Developer Portal, which provides comprehensive documentation and tutorials for building decentralized applications on Ethereum. Learning Solidity is essential for anyone who wants to develop smart contracts. There are many resources available online, including Solidity documentation, online courses, and tutorials. It's also helpful to join online communities like the Ethereum Stack Exchange and the Solidity Gitter channel, where you can ask questions and get help from other developers.
Choosing the Right Resources to Learn
Selecting the appropriate resources for learning smart contracts is crucial for a smooth and effective learning journey. With the abundance of information available online, it's important to filter through the noise and focus on reliable and reputable sources. Start by exploring introductory courses and tutorials that provide a high-level overview of smart contracts and their applications. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and ed X offer a variety of courses taught by experts in the field. This is how to get started with what are smart contracts today.
These courses often cover the fundamentals of blockchain technology, smart contract programming languages like Solidity, and the process of deploying and interacting with smart contracts. Once you have a solid understanding of the basics, you can delve deeper into more advanced topics like smart contract security, gas optimization, and decentralized application (d App) development. For those who prefer a more hands-on approach, consider participating in coding bootcamps or workshops that provide practical experience in building and deploying smart contracts. These programs often involve working on real-world projects and collaborating with other developers, which can accelerate your learning and help you build a portfolio. In addition to formal courses and programs, it's also essential to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in the smart contract ecosystem by following industry blogs, attending conferences, and engaging with online communities. Platforms like Medium, Twitter, and Reddit are great resources for staying informed about the latest trends and innovations in the field. Remember, learning smart contracts is an ongoing process, so be patient, persistent, and always eager to explore new concepts and technologies.
Tips for Writing Secure Smart Contracts
Security is paramount when writing smart contracts, as vulnerabilities can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage. Smart contracts are immutable, meaning that once they are deployed, they cannot be easily modified or patched. Therefore, it's crucial to write secure code from the outset. One of the most important tips for writing secure smart contracts is to follow the principle of least privilege, which means granting users only the minimum necessary permissions to perform their tasks. This can help prevent unauthorized access and manipulation of the contract. Another important tip is to thoroughly test your smart contracts before deploying them to the mainnet. This includes writing unit tests to verify the functionality of individual functions and integration tests to ensure that the contract interacts correctly with other contracts and systems. This is how to get started with what are smart contracts today.
It's also important to use static analysis tools to identify potential vulnerabilities in your code. Static analysis tools can automatically scan your code for common security flaws, such as integer overflows, reentrancy attacks, and denial-of-service vulnerabilities. In addition to these technical measures, it's also important to adopt a security-conscious mindset when writing smart contracts. This means being aware of the potential risks and vulnerabilities and taking steps to mitigate them. For example, it's important to avoid using predictable random number generators, as these can be easily exploited by attackers. It's also important to be careful when handling user input, as this can be a source of vulnerabilities. Finally, it's important to keep your smart contracts up-to-date with the latest security patches and best practices. The smart contract ecosystem is constantly evolving, and new vulnerabilities are discovered all the time. Therefore, it's essential to stay informed and take steps to protect your contracts from known threats.
Understanding Common Vulnerabilities
A deep understanding of common smart contract vulnerabilities is essential for writing secure and reliable code. One of the most prevalent vulnerabilities is the reentrancy attack, which occurs when a malicious contract calls back into the vulnerable contract before the first invocation is completed. This can allow the attacker to drain funds from the contract or manipulate its state. To prevent reentrancy attacks, it's important to follow the "checks-effects-interactions" pattern, which means performing all necessary checks before making any state changes and then interacting with external contracts. This is how to get started with what are smart contracts today!
Another common vulnerability is the integer overflow, which occurs when an integer variable exceeds its maximum value, causing it to wrap around to a small value. This can lead to unexpected behavior and can be exploited by attackers to manipulate the contract's logic. To prevent integer overflows, it's important to use safe math libraries that perform overflow checks before performing arithmetic operations. Another important vulnerability to be aware of is the denial-of-service (Do S) attack, which occurs when an attacker overwhelms the contract with requests, making it unavailable to legitimate users. To prevent Do S attacks, it's important to limit the number of gas that can be consumed by a single transaction and to implement rate limiting to prevent attackers from flooding the contract with requests. In addition to these vulnerabilities, it's also important to be aware of other common security flaws, such as timestamp dependence, predictable random number generators, and delegatecall vulnerabilities. By understanding these vulnerabilities and taking steps to mitigate them, you can significantly improve the security of your smart contracts.
Fun Facts About Smart Contracts
Did you know that the first smart contract was likely a vending machine? While Nick Szabo formalized the concept, the basic idea of automated agreements has been around for much longer. Vending machines accept payment and automatically dispense a product – a simple but effective example of a pre-programmed agreement. It goes without saying this is how to get started with what are smart contracts today, right?
Another fun fact is that smart contracts are not actually "smart" in the AI sense. They don't learn or adapt on their own. They simply execute pre-defined instructions based on specific conditions. The "smart" part comes from the cleverness of the code and the logic behind it.
Smart contracts are also surprisingly versatile. They're not just for financial applications. They can be used in various industries, including supply chain management, healthcare, real estate, and even voting systems. The possibilities are endless. One of the most interesting developments in the smart contract space is the emergence of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). DAOs are organizations that are governed by rules encoded in smart contracts. This allows for more democratic and transparent decision-making processes. However, DAOs also face challenges in terms of governance and security. Despite these challenges, DAOs have the potential to revolutionize the way organizations are structured and managed. Furthermore, Smart contracts are constantly evolving and becoming more sophisticated. Researchers are working on new programming languages, formal verification methods, and security tools to improve the reliability and security of smart contracts. As the technology matures, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of smart contracts in the future.
How to Deploy Your First Smart Contract
Deploying your first smart contract might seem daunting, but it's actually a straightforward process with the right tools and guidance. The first step is to choose a platform for deploying your contract. Ethereum is the most popular platform for smart contracts, but other options include Binance Smart Chain, Cardano, and Solana. Once you've chosen a platform, you'll need to set up a development environment. This typically involves installing a programming language like Solidity, a development framework like Truffle or Hardhat, and a wallet like Meta Mask. This is how to get started with what are smart contracts today!
After you've set up your development environment, you can write your smart contract code. It's important to write secure and well-tested code to avoid vulnerabilities. Once you've written your code, you can compile it using a Solidity compiler. Compiling your code translates it into bytecode, which is the code that is executed on the blockchain. After you've compiled your code, you can deploy it to the blockchain using a deployment tool like Truffle or Hardhat. Deploying your contract involves paying a transaction fee (gas) to the network to execute the deployment transaction. Once your contract is deployed, it's publicly accessible on the blockchain and can be interacted with by anyone. You can interact with your contract using a wallet like Meta Mask or a web application that you build. Deploying your first smart contract is a rewarding experience that can give you a deeper understanding of how blockchain technology works. It's also a great way to start building your own decentralized applications.
What If Smart Contracts Fail?
What happens when a smart contract goes wrong? This is a critical question that highlights the importance of careful development, testing, and auditing. Because smart contracts are immutable, once they are deployed, they cannot be easily changed. This means that if there is a bug or vulnerability in the code, it can be very difficult or impossible to fix. The consequences of a smart contract failure can be severe, ranging from financial losses to legal liabilities. This is how to get started with what are smart contracts today!
One example of a smart contract failure is the DAO hack, which occurred in 2016. The DAO was a decentralized autonomous organization that was designed to invest in Ethereum projects. However, a vulnerability in the DAO's smart contract allowed an attacker to drain millions of dollars worth of ether. The DAO hack highlighted the risks of deploying complex and untested smart contracts. In response to the DAO hack, the Ethereum community decided to hard fork the blockchain to reverse the transaction and return the funds to the DAO's investors. However, this decision was controversial and led to the creation of Ethereum Classic, a separate blockchain that preserved the original, un-forked version of Ethereum. The DAO hack serves as a cautionary tale about the importance of smart contract security. It also demonstrates the potential for blockchain governance to be contentious and divisive. The risks involved mean that careful development is necessary.
Listicle of Smart Contract Use Cases
Here's a list of interesting smart contract use cases to inspire you:
1.Decentralized Finance (De Fi): Lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming without intermediaries.
2.Supply Chain Management: Tracking goods from origin to delivery for transparency and accountability.
3.Digital Identity: Securely managing and verifying digital identities.
4.Voting Systems: Secure and transparent online voting.
5.Real Estate: Automating property transactions and managing rental agreements.
6.Healthcare: Securely storing and sharing medical records.
7.Gaming: Creating decentralized in-game economies and managing virtual assets.
8.Insurance: Automating claims processing and fraud detection.
9.Intellectual Property: Protecting and managing intellectual property rights.
10.Royalty Payments: Automating royalty payments to artists and creators.
This is how to get started with what are smart contracts today!
Question and Answer Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about smart contracts:
Q: Do I need to be a coding expert to understand smart contracts?
A: Not necessarily! While coding knowledge is helpful for writing and deploying smart contracts, you can still understand the fundamental concepts and use cases without being a programmer. Start with introductory resources that explain the basics in plain language.
Q: Are smart contracts legally binding?
A: The legal status of smart contracts is still evolving. While some jurisdictions recognize smart contracts as legally binding agreements, others do not. It's important to consult with legal professionals to understand the legal implications of using smart contracts in your specific situation.
Q: Are smart contracts secure?
A: Smart contracts can be secure, but they are not immune to vulnerabilities. It's crucial to follow security best practices and thoroughly test and audit your smart contracts before deploying them.
Q: What are the limitations of smart contracts?
A: Smart contracts have limitations, such as their immutability, limited access to external data, and the potential for gas fees to fluctuate. It's important to be aware of these limitations when designing and deploying smart contracts.
Conclusion of How to Get Started with What Are Smart Contracts? Today
Smart contracts are a powerful technology with the potential to revolutionize various industries. While getting started can seem intimidating, with the right resources and a willingness to learn, anyone can unlock the potential of this transformative technology. Embrace the learning process, experiment with different platforms and tools, and stay curious. The future of smart contracts is bright, and you can be a part of it!