Ever wondered how those lines of code magically materialize onto the blockchain, turning into fully functional smart contracts? It's a fascinating process, but also one that can seem daunting if you're just starting out. Forget complex jargon and confusing workflows – let's break down the current landscape of smart contract deployment and make it accessible for everyone.
Diving into the world of smart contract deployment can feel like navigating a labyrinth. You're faced with a mountain of tools, various platforms, and the pressure of ensuring your code is not only functional but also secure from potential vulnerabilities. It can be overwhelming trying to figure out where to begin, which tools are right for you, and how to avoid common pitfalls that can lead to costly mistakes.
This guide is designed to be your friendly companion as you embark on your smart contract deployment journey. We'll explore the common methods used today, break down the tools you'll need, and provide a clear path to get you started with confidence. We'll cover everything from setting up your development environment to understanding the different deployment strategies and best practices for security.
This article provides a simplified overview of smart contract deployment, focusing on practical steps for beginners. We'll delve into popular tools like Remix IDE and Truffle, explore deployment networks (testnets and mainnet), discuss security considerations, and offer tips for successful deployments. Ultimately, you'll gain the knowledge to confidently deploy your own smart contracts and contribute to the exciting world of blockchain development.
My First Foray into Smart Contract Deployment
My initial encounter with smart contract deployment was, to put it mildly, a bit of a baptism by fire. Fresh out of a Solidity tutorial, I was eager to deploy my "revolutionary" token contract. Armed with a simple Remix IDE setup and a burning desire to conquer the blockchain, I dove headfirst into the process. I breezed through the coding, confident that my masterpiece was ready for the world. Then came the moment of truth: deployment. The initial attempt failed miserably due to insufficient gas. I scrambled to adjust the gas limit, re-deployed, and...success! Or so I thought. A few hours later, I noticed a glaring vulnerability in my code, one that could have allowed someone to drain all the tokens. Thankfully, it was just on a testnet, but the experience was a stark reminder that deploying smart contracts is much more than just writing code. It requires careful planning, thorough testing, and a strong understanding of security best practices. That experience motivated me to delve deeper into the intricacies of deployment tools, security audits, and gas optimization techniques. Now, I approach deployments with a healthy dose of caution and a much more structured approach, realizing that the real challenge lies not just in creating a smart contract, but in ensuring its safe and reliable execution on the blockchain.
What Does "Deployment" Actually Mean?
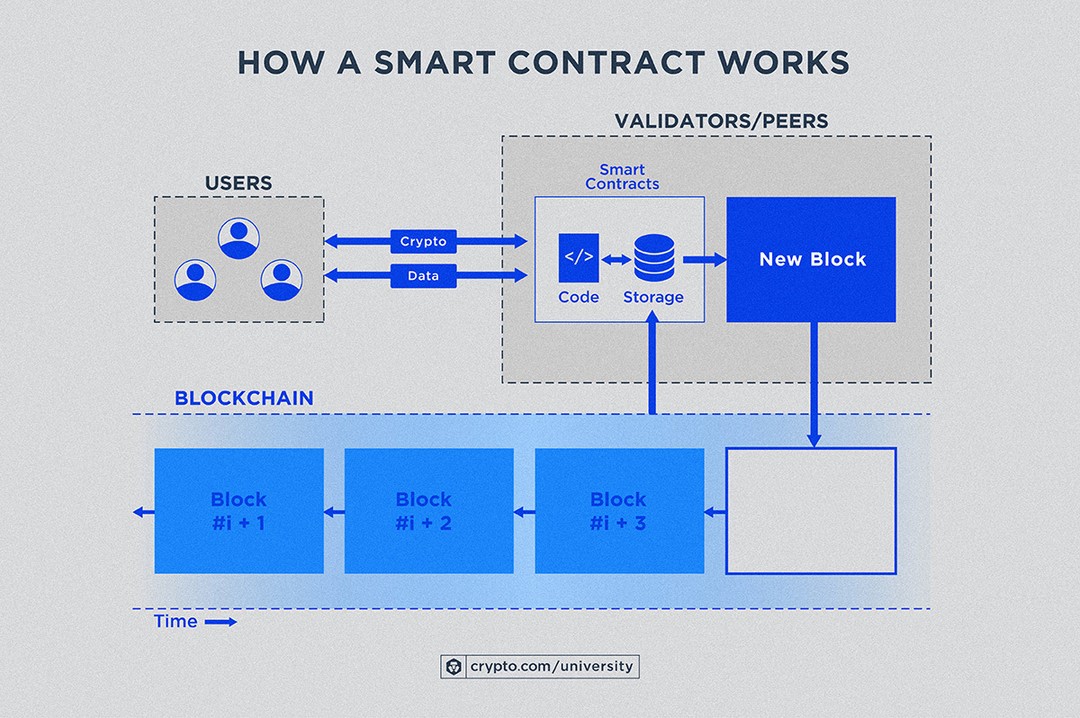
Deployment, in the context of smart contracts, is the process of making your compiled code available and executable on a blockchain network. It involves taking your smart contract code (written in languages like Solidity), compiling it into bytecode, and then submitting a transaction to the blockchain that creates a new instance of your contract. This transaction essentially registers your contract's bytecode at a specific address on the blockchain. From that point on, anyone can interact with your contract by sending transactions to that address, triggering the functions defined within your code. Think of it like installing a software program on a computer. The deployment process is akin to installing the program on the blockchain, making it accessible and executable by anyone with the necessary permissions. This also entails assigning storage space within the blockchain's state to hold the contract's data, such as variable values and mappings. The process involves paying a transaction fee (gas) to compensate the network for the computational resources used to execute the deployment transaction. Selecting the appropriate network (testnet for development, mainnet for production) is also a critical part of deployment. Successful deployment results in a permanent and immutable instance of your smart contract on the blockchain, ready to be interacted with.
The History and Evolution of Smart Contract Deployment
The concept of smart contracts predates blockchain technology, with Nick Szabo introducing the idea in the 1990s. However, it was the advent of Ethereum in 2015 that truly brought smart contracts to life. Initially, deploying smart contracts was a relatively manual and cumbersome process, often requiring developers to directly interact with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and craft transactions by hand. Early tools like the Ethereum Wallet offered basic deployment functionalities, but lacked the sophistication and developer-friendliness of modern solutions. Over time, the development ecosystem matured, leading to the emergence of powerful frameworks like Truffle, Hardhat, and Brownie. These frameworks automated many of the tedious aspects of deployment, such as compilation, migration, and testing. They also introduced features like dependency management and standardized project structures, making it easier for developers to collaborate and build complex decentralized applications. As the industry evolved, deployment strategies also became more sophisticated, with a greater emphasis on security audits, formal verification, and gas optimization. Multi-sig wallets and governance mechanisms were increasingly used to manage contract upgrades and mitigate risks. Today, deployment is a complex and multifaceted process that requires a deep understanding of both the technical and security aspects of smart contract development. The myths surrounding deployment often involve the idea that it's a simple "one-click" process, when in reality, it demands meticulous planning and execution.
Unlocking the Secrets of Successful Deployment
The hidden secret to successful smart contract deployment isn't about using the most advanced tools or writing the most complex code; it's about meticulous planning and attention to detail. It starts with a thorough understanding of your contract's functionality, the potential attack vectors, and the gas costs associated with different operations. Before even touching the deployment button, you should have conducted rigorous testing on local development environments and testnets. This includes unit tests, integration tests, and security audits. Pay close attention to gas optimization techniques to minimize deployment costs and improve the overall efficiency of your contract. Understand the implications of different storage patterns and function modifiers. Another crucial aspect is managing your private keys securely. Never expose your private keys directly in your code or commit them to version control. Use hardware wallets or secure key management services to protect your credentials. Furthermore, consider using a multi-sig wallet for contract ownership to prevent single points of failure. Finally, stay updated with the latest security vulnerabilities and best practices in the smart contract development community. Regularly review your code and dependencies for potential weaknesses. By focusing on these often overlooked details, you can significantly increase your chances of a successful and secure deployment. The "secret" is, in essence, diligence and a proactive approach to security.
Recommendations for Streamlining Your Deployment Process
For newcomers to smart contract deployment, I strongly recommend starting with Remix IDE for initial experimentation. It's a browser-based IDE that allows you to write, compile, and deploy smart contracts directly in your web browser, without the need for any local setup. Once you're comfortable with the basics, transition to a more robust framework like Truffle or Hardhat. These frameworks provide a structured development environment, automated testing capabilities, and migration scripts for managing deployments across different networks. Consider using Infura or Alchemy for reliable access to Ethereum nodes, especially when deploying to testnets or mainnet. For security audits, explore reputable firms like Consen Sys Diligence or Trail of Bits. Regularly participate in online communities and forums to learn from experienced developers and stay updated with the latest best practices. When deploying to mainnet, always prioritize security audits and gas optimization. Consider using a multi-sig wallet for contract ownership and implement a robust upgrade mechanism. Furthermore, thoroughly test your contract on a testnet like Goerli or Sepolia before deploying to mainnet. Remember that smart contract deployment is an iterative process. Don't be afraid to experiment, make mistakes, and learn from your experiences. By following these recommendations, you can significantly streamline your deployment process and increase your chances of success.
Understanding Different Deployment Networks (Testnets vs. Mainnet)
A critical aspect of smart contract deployment is understanding the difference between testnets and mainnet. Testnets are essentially replica blockchains that mimic the functionality of the main Ethereum network, but use "fake" Ether (ETH) that has no real-world value. They are designed for testing and development purposes, allowing developers to experiment with their smart contracts without risking real funds. Common Ethereum testnets include Goerli, Sepolia, and others, each with slightly different characteristics and genesis states. Deploying to a testnet is a crucial step in the development process, as it allows you to identify bugs, vulnerabilities, and gas optimization opportunities before deploying to the live network. You can obtain testnet ETH from various faucets, which are websites or services that distribute small amounts of test ETH for free. Mainnet, on the other hand, is the "real" Ethereum blockchain where transactions involve real ETH. Deploying to mainnet is a significant step that should only be taken after thorough testing and security audits. Once a smart contract is deployed to mainnet, it is immutable (unless designed with an upgrade mechanism) and can be interacted with by anyone in the world. The transaction fees on mainnet are typically much higher than on testnets, as they reflect the real-world demand for block space. Choosing the appropriate network for your deployment is crucial. Use testnets for development and testing, and reserve mainnet for production deployments only after rigorous validation.
Essential Tips for a Smooth Smart Contract Deployment
Achieving a seamless smart contract deployment isn't just about the technical aspects; it's also about adopting a strategic mindset and employing best practices. Firstly, always start with a well-defined specification of your smart contract's functionality and requirements. This will serve as a roadmap for your development and testing efforts. Secondly, thoroughly test your smart contract using a variety of test cases, including edge cases and potential attack vectors. Use automated testing frameworks like Truffle or Hardhat to streamline this process. Thirdly, optimize your code for gas efficiency to minimize deployment costs and improve the overall performance of your contract. Consider using techniques like storage packing, function modifiers, and efficient loop structures. Fourthly, secure your private keys with a hardware wallet or a secure key management service. Never expose your private keys directly in your code or commit them to version control. Fifthly, conduct a security audit of your smart contract by a reputable firm before deploying to mainnet. This will help identify potential vulnerabilities and prevent costly exploits. Sixthly, monitor your deployed contract for unexpected behavior or anomalies. Use blockchain explorers and monitoring tools to track transaction activity and gas consumption. Finally, stay updated with the latest security best practices and vulnerabilities in the smart contract development community. By following these essential tips, you can significantly increase your chances of a smooth and successful smart contract deployment.
Understanding Gas and Gas Optimization
Gas, in the context of Ethereum, is the unit of measurement for the computational effort required to execute specific operations on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Every transaction on the Ethereum network, including smart contract deployments and function calls, requires a certain amount of gas. Users pay for this gas in ETH, the native cryptocurrency of Ethereum. The gas price, which is the amount of ETH paid per unit of gas, fluctuates based on network congestion. Gas optimization is the process of minimizing the amount of gas required to execute a smart contract. This is crucial for reducing deployment costs and improving the overall efficiency of your contract. There are several techniques you can use to optimize gas consumption. These include using storage packing to minimize the amount of storage space required, employing efficient loop structures to reduce computational overhead, and using function modifiers to restrict access to certain functions. Additionally, consider using the "immutable" keyword for variables that are only set during contract creation, as this can save gas compared to using "constant". Always test your contract's gas consumption using tools like Remix IDE or Hardhat's gas reporter. Furthermore, stay updated with the latest gas optimization techniques and best practices in the Solidity development community. By mastering gas optimization, you can create more efficient and cost-effective smart contracts.
Fun Facts About Smart Contract Deployment
Did you know that the very first smart contract deployed on Ethereum was a simple token contract? It paved the way for the explosion of ERC-20 tokens that we see today. Another fun fact is that the largest smart contract deployment in terms of gas consumption involved a complex decentralized exchange (DEX). Deploying such a complex contract can cost a significant amount of ETH in gas fees. Furthermore, some smart contracts have been deployed accidentally to the wrong network (e.g., deploying to mainnet instead of a testnet), resulting in wasted gas and potential security risks. It's also interesting to note that the size of a smart contract can impact its deployment cost, as larger contracts require more gas to store on the blockchain. Some developers have even created "minimalist" smart contracts designed to be as small and gas-efficient as possible. Another fun fact is that the Ethereum network has undergone several hard forks that have impacted the way smart contracts are deployed and executed. These forks have introduced new opcodes and gas costs, requiring developers to adapt their code accordingly. Finally, the world of smart contract deployment is constantly evolving, with new tools, techniques, and best practices emerging all the time. Staying updated with the latest developments is crucial for any smart contract developer.
How to Ensure a Secure Deployment
Ensuring a secure smart contract deployment is paramount to protecting your code and users' funds. It's a multi-faceted process that requires a combination of secure coding practices, thorough testing, and independent security audits. Start by following secure coding guidelines, such as avoiding common vulnerabilities like reentrancy, integer overflow, and timestamp dependence. Use static analysis tools like Slither or Mythril to automatically detect potential vulnerabilities in your code. Conduct rigorous unit testing and integration testing to ensure that your contract functions as expected under various conditions. Deploy your contract to a testnet and conduct thorough penetration testing to identify any weaknesses that might be exploited by attackers. Engage a reputable security audit firm to conduct an independent review of your code. They will use their expertise to identify potential vulnerabilities and provide recommendations for remediation. Before deploying to mainnet, consider implementing a bug bounty program to incentivize security researchers to find and report vulnerabilities in your code. Use a multi-sig wallet for contract ownership to prevent single points of failure. Implement a robust upgrade mechanism to allow you to fix bugs and deploy new features without disrupting existing users. Monitor your deployed contract for suspicious activity and anomalies. By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of a security breach and ensure a more secure deployment.
What If a Deployment Goes Wrong?
Even with the best planning and precautions, smart contract deployments can sometimes go wrong. A failed deployment can result in wasted gas, a non-functional contract, or even a vulnerable contract that can be exploited. If a deployment fails due to insufficient gas, you can try increasing the gas limit and redeploying. However, be careful not to set the gas limit too high, as you will be charged for the unused gas. If a deployment fails due to a bug in your code, you will need to fix the bug and redeploy the contract. However, if the contract is already deployed to mainnet and is immutable, you may not be able to fix the bug directly. In this case, you may need to deploy a new version of the contract and migrate users to the new version. If a deployment results in a vulnerable contract, you may need to take immediate action to mitigate the risk. This could involve pausing the contract, transferring funds to a safe location, or deploying a patch contract. In some cases, you may need to seek legal advice or consult with security experts. It's important to have a contingency plan in place to deal with potential deployment failures. This plan should include procedures for identifying, diagnosing, and resolving deployment issues. By being prepared for the worst, you can minimize the impact of a failed deployment and protect your users' funds.
Top 5 Things to Remember When Deploying a Smart Contract
Deploying a smart contract can be tricky, so keep these five things in mind:
1.Thorough Testing is Key: Never deploy without rigorous testing on a testnet. This includes unit tests, integration tests, and security audits.
2.Gas Optimization Matters: Optimize your code for gas efficiency to minimize deployment costs and transaction fees.
3.Secure Your Keys: Protect your private keys with a hardware wallet or secure key management service.
4.Monitor Your Contract: After deployment, monitor your contract for unexpected behavior or anomalies.
5.Stay Informed: Stay updated with the latest security best practices and vulnerabilities in the smart contract development community. By remembering these five things, you can significantly increase your chances of a successful and secure deployment.
Question and Answer About How to Get Started with How Smart Contracts Are Deployed Today
Here are some common questions and answers about smart contract deployment:
Q: What is the difference between a testnet and mainnet?
A: Testnets are replica blockchains used for testing, while mainnet is the live Ethereum network where real transactions occur.
Q: How do I get testnet ETH?
A: You can obtain testnet ETH from various faucets, which are websites that distribute small amounts of test ETH for free.
Q: What tools can I use to deploy a smart contract?
A: Popular tools include Remix IDE, Truffle, and Hardhat.
Q: How much does it cost to deploy a smart contract?
A: The cost depends on the size of the contract, the complexity of the code, and the current gas price on the Ethereum network.
Conclusion of How to Get Started with How Smart Contracts Are Deployed Today
Smart contract deployment, while initially intimidating, becomes more manageable with a structured approach. By understanding the tools, networks, and security considerations involved, you can confidently deploy your own smart contracts and contribute to the exciting world of blockchain development. Remember to prioritize testing, security audits, and gas optimization. Embrace the iterative nature of the process, learn from your experiences, and stay updated with the latest best practices in the community. Happy deploying!